[dwdocp05-240611-01.tif, 1, en_US]
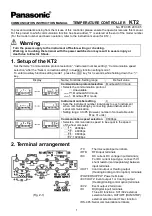
Figure 7-100
Parallel Line with Transformers
Stage ▶:
Stage:
T:
Directional stage, forward direction set
Non-directional stage
Grading time
Application Notes for Directional Comparison Protection
The direction determination of directional overcurrent protection can be used to implement directional
comparison protection for cable runs with infeed at both ends. Directional comparison protection is used for
the selective isolation of a faulted line section (for example, subsections of closed rings). Sections are isolated
in fast time, that is, they do not suffer the disadvantage of long grading times.
This technique requires that directional information can be exchanged between the individual protection
stations. You can implement this information exchange using a communication channel (protection interface
or IEC 61850 GOOSE) or with pilot wires for signal transmission via an auxiliary voltage loop.
Protection Principle
The protection principle is shown in
. 2 devices (one at the start of the line and the other at the
end of the line) work together in each line section. The information fault in forward direction is transferred
between them. A directional definite-time overcurrent protection level is in operation in both devices in the
forward direction (1st level). However, this level is not enabled in the idle state. The level is only released
when the information fault in forward direction is received from the opposite end. If the enabled level also
defines the fault in the forward direction, the fault must be on this line section and the level trips immediately.
As this protection principle works with an enable procedure (and not with a blocking procedure), there is no
need to delay the level.
A second directional definite-time overcurrent protection stage with standard time grading works in parallel
with the first stage as a selective backup stage. This ensures full selectivity of protection in the following situa-
tions:
•
Infeed at one end or weak infeed at one end: In this case, no release signal is generated.
•
Failure of the communication route: In this case, the release signal is not transmitted.
To provide selective protection in fast time for busbars between the line sections also, you can combine this
protection principle with the principle of reverse interlocking. This principle is not discussed in further detail in
this document.
7.6.10
Protection and Automation Functions
7.6 Directional Overcurrent Protection, Phases
698
SIPROTEC 5, High-Voltage Bay Controller, Manual
C53000-G5040-C015-9, Edition 11.2017
Summary of Contents for 6MD85
Page 8: ...8 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 30: ...30 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 46: ...46 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 172: ...172 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 514: ...514 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 1056: ...1056 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 1092: ...1092 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 1204: ...1204 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 1238: ...1238 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 1252: ...1252 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...
Page 1256: ...1256 SIPROTEC 5 High Voltage Bay Controller Manual C53000 G5040 C015 9 Edition 11 2017 ...