Functional Description
915
SLAU723A – October 2017 – Revised October 2018
Copyright © 2017–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Ethernet Controller
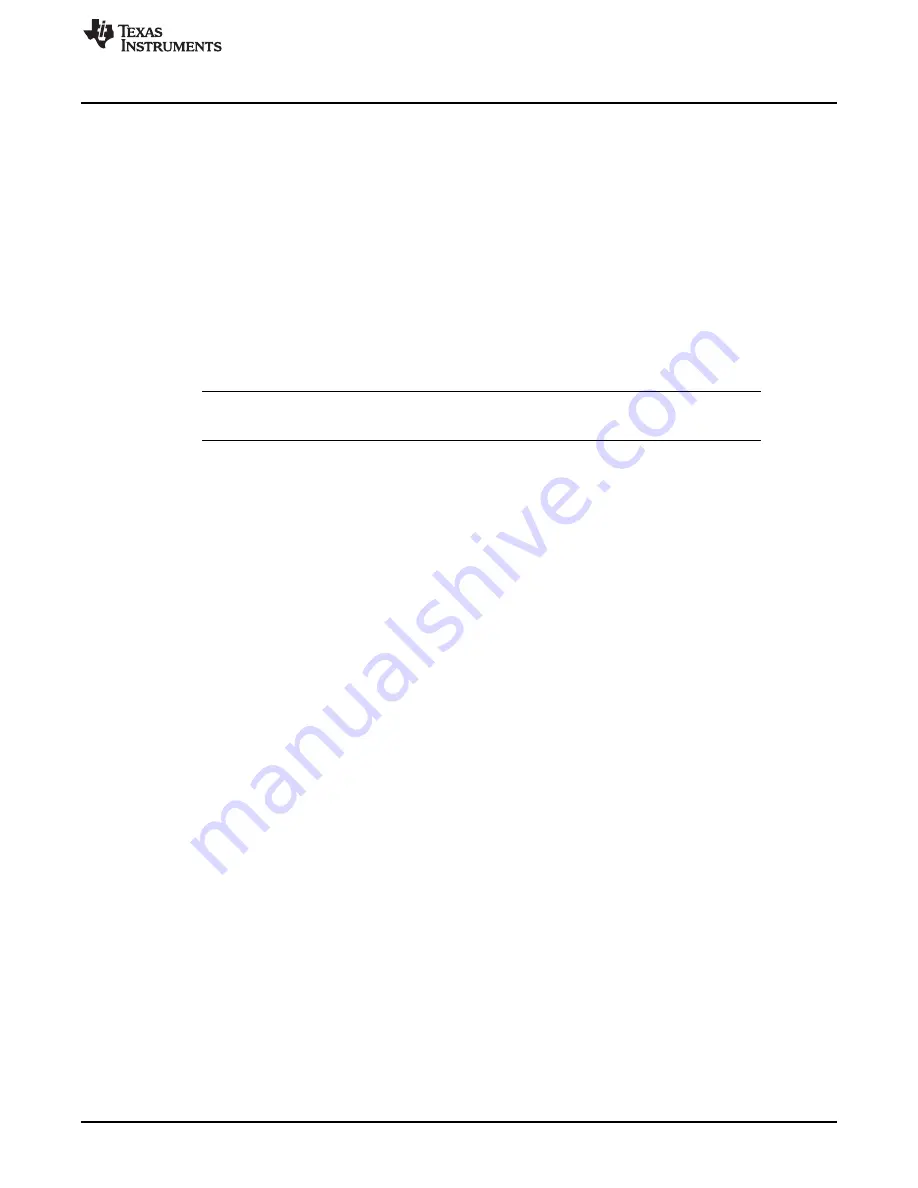
G(x) = x
32
+ x
26
+ x
23
+ x
22
+ x
16
+ x
12
+ x
11
+ x
10
+ x
8
+ x
7
+ x
5
+ x
4
+ x
2
+ x + 1
(49)
The calculated CRC is valid on the next clock after the data is received.
15.3.5.5 MAC Receive Frame Controller
If the RA bit is set in the Ethernet MAC Frame Filter (EMACFRAMEFLTR) register, offset 0x004, the MAC
Receive Frame Controller initiates the data transfer to the RX FIFO as soon as four bytes of Ethernet data
are received. At the end of the data transfer, the received frame status that includes the frame filter bits
(SA or DA filter fail) and status are also sent. These bits indicate to the application whether the received
frame has passed the filter controls. This module does not drop any frame on its own in this mode.
If the RA bit is clear, the MAC Receive Frame Controller performs frame filtering based on the
destination/source address (the application still needs to perform another level of filtering if it decides not
to receive any bad frames like runt, CRC error frames, etc.) After receiving the destination or source
address bytes, the MAC Receive Frame Controller checks the filter-fail sign for an address match. On
detecting a filter-fail, the frame is dropped and not transferred to the application.
NOTE:
When the PMT module is configured for power-down mode, all received frames are dropped
and not forwarded to the application.
15.3.6 IEEE 1588 and Advanced Timestamp Function
The MAC module supports the IEEE 1588-2002 Timestamp Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and the IEEE
1588-2008 Advanced Timestamp features. PTP enables precise synchronization of clocks in
measurement and control systems implemented with technologies such as network communication, local
computing, and distributed objects. The PTP applies to systems communicating by a local area network
supporting multicast messaging. This protocol enables heterogeneous systems that include clocks of
varying inherent precision, resolution, and stability to synchronize. The protocol supports system-wide
synchronization accuracy in the sub-microsecond range with minimal network and local clock computing
resources.
The PTP is transported over UDP/IP. The system or network is classified into master and slave nodes for
distributing the timing and clock information.
shows the process that PTP uses for
synchronizing a slave node to a master node by exchanging PTP messages.
















































