Functional Description
1527
SLAU723A – October 2017 – Revised October 2018
Copyright © 2017–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Quad Synchronous Serial Interface (QSSI)
NOTE:
SPO = 0 and SPH = 0 is the only frame structure allowed for advanced, bi- and quad-SSI
modes.
Different transactions can follow one another in the FIFOs. The following transaction combinations are
allowed:
•
Legacy SSI mode (if configured for this mode, switching to any other alternate mode is not
recommended)
•
Advanced SSI mode followed by bi-SSI mode
•
Advanced SSI mode followed by quad-SSI mode
•
Advanced SSI mode followed by bi-SSI mode followed by advanced SSI mode
•
Advanced SSI mode followed by quad-SSI mode followed by advanced SSI mode
Note that switching between Quad-SSI and bi-SSI is not encouraged in a single transaction.
23.3.4 SSInFSS Function
For enhanced modes of operation, the SSInFss signal can be programmed to assert low at the start of
each byte transfer for one clock or the entire frame. This is configured by programming the FSSHLDFRM
bit in the SSICR1 register. The EOM bit is also provided to signify end of frame transmission. This bit is
embedded in the TXFIFO entry for use at the interface to deassert SSInFss at the appropriate time. The
FSSHLDFRM bit can also be used when operating in 8-bit legacy SSI mode.
The functionality of the FSSHLDFRM bit for both legacy SSI mode and the enhanced modes are as
follows:
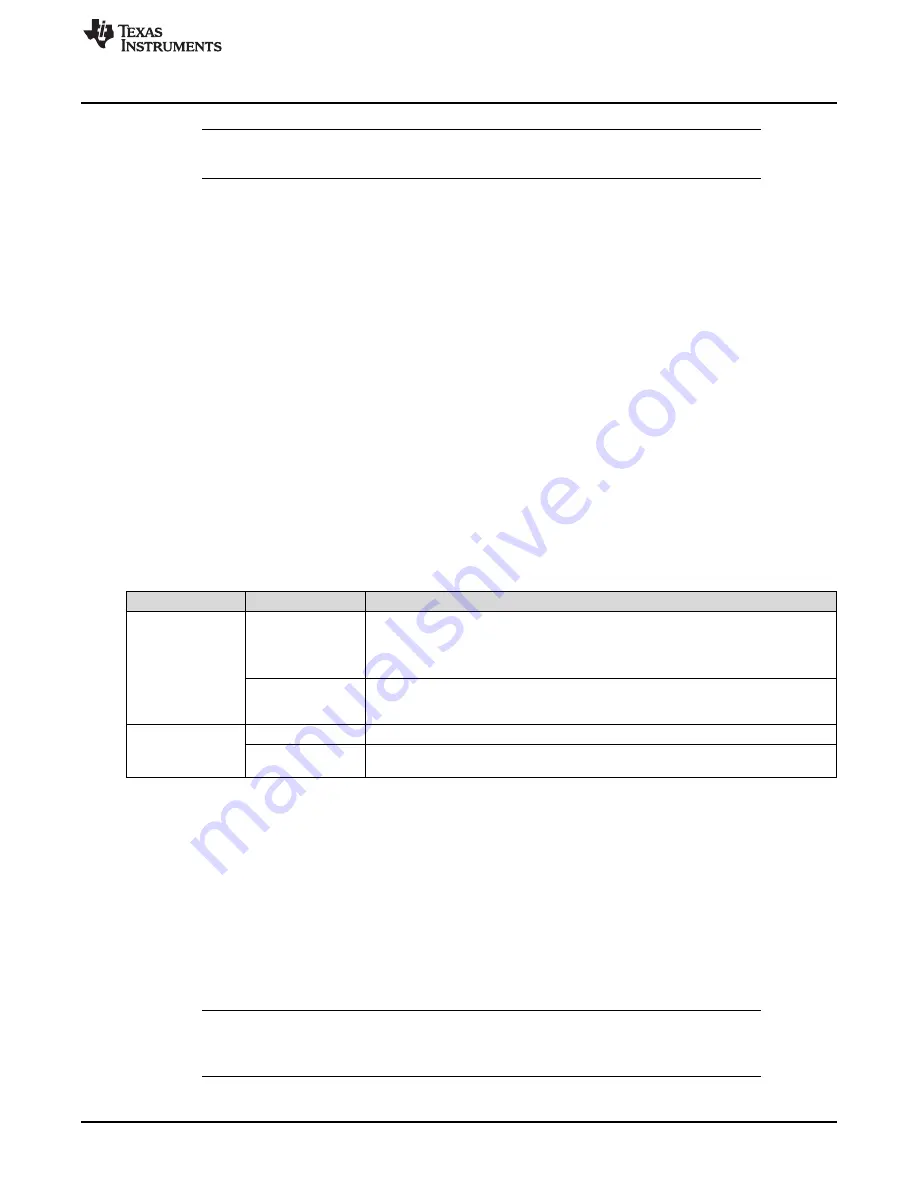
Table 23-2. SSInFss Functionality
Mode
FSSHLDFRM
Description
Legacy mode
0
For Freescale format, with SPH = 0, the SSInFss signal is deasserted (high) between
continuous transfers. For SPH = 1, the SSInFss signal is asserted (low) between
continuous transfers.
For TI format, the SSInFss signal is deasserted (high) after every data transfer.
1
Not a valid combination as the SSInFSS signal is forced low even after transmission is
completed and requires the FSSHLDFRM bit to be cleared to release the SSInFSS
signal.
Advanced, bi-, and
quad-SSI mode
0
SSInFss is asserted low after every byte of data
1
New data written to the TX FIFO notifies SSInFss to assert low until the EOM bit is set
with the last transfer, only after which the SSInFSS is asserted high.
23.3.5 High Speed Clock Operation
In master mode, QSSI module can enable a high speed clock by setting the HSCLKEN bit in the SSI
Control 1 (SSICR1) register. In this mode of operation, SSInCLK from the QSSI master operation is
reflected back as a loopback clock, HSPEEDCLK, to the QSSI module. This allows faster timing since the
logic can be used to adjust clock to external data relationships. HSPEEDCLK captures RX data in a
separate register. This allows the time between the clock as seen by a remote device and the internal
clock to match more closely.
Receive data is captured in a separate register sampled on loop-back clock (HSPEEDCLK) and the RX
FIFO write control registered on HSPEEDCLK. If the HSCKEN = 1, the corresponding shift register and
FIFO write enable will be selected for use. This supports faster QSSI master speed.
NOTE:
For proper functionality of high speed mode, the HSCLKEN bit in the SSICR1 register
should be set before any SSI data transfer or after applying a reset to the QSSI module. In
addition, the SSE bit must be set to 0x1 before the HSCLKEN bit is set.






























