EPI Registers
1137
SLAU723A – October 2017 – Revised October 2018
Copyright © 2017–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
External Peripheral Interface (EPI)
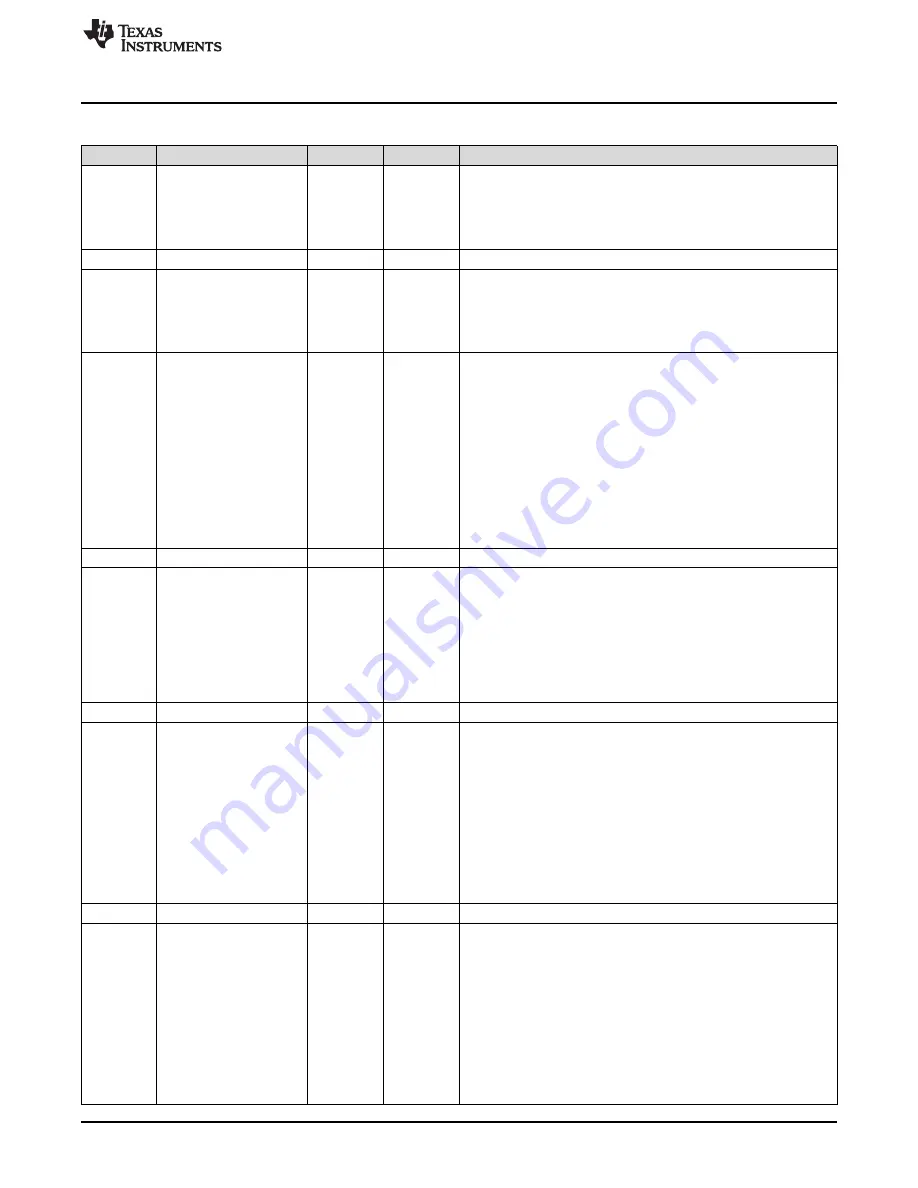
Table 16-20. EPIGPCFG Register Field Descriptions (continued)
Bit
Field
Type
Reset
Description
30
CLKGATE
R/W
0x0
Clock Gated CLKGATE is ignored if CLKPIN is 0 or if the COUNT0
field in the EPIBAUD register is cleared.
0x0 = The EPI clock is free running.
0x1 = The EPI clock is output only when there is data to write or
read (current transaction); otherwise the EPI clock is held low.
29-27
RESERVED
R
0x0
26
FRM50
R/W
0x0
50/50 Frame
0x0 = The FRAME signal is output as a single pulse, and then held
low for the count.
0x1 = The FRAME signal is output as 50/50 duty cycle using count
(see FRMCNT).
25-22
FRMCNT
R/W
0x0
Frame Count This field specifies the size of the frame in EPI clocks.
The frame counter is used to determine the frame size.
The count is 1.
So, a FRMCNT of 0 forms a pure transaction valid signal (held high
during transactions, low otherwise).
A FRMCNT of 0 with FRM50 set inverts the FRAME signal on each
transaction.
A FRMCNT of 1 means the FRAME signal is inverted every other
transaction
a value of 15 means every sixteenth transaction.
If FRM50 is set, the frame is held high for 1 transactions,
then held low for that many transactions, and so on.
If FRM50 is clear, the frame is pulsed high for one EPI clock and
then low for FRMCNT EPI clocks.
21-20
RESERVED
R
0x0
19
WR2CYC
R/W
0x0
2-Cycle Writes When this bit is set, then the RW bit is forced to be
set.
0x0 = Data is output on the same EPI clock cycle as the address.EPI
clock begins toggling one cycle before the WR strobe goes High.
0x1 = Writes are two EPI clock cycles long, with address on one EPI
clock cycle (with the WR strobe asserted) and data written on the
following EPI clock cycle (with WR strobe deasserted). The next
address (if any) is in the cycle following.If the WR2CYC bit is set, the
EPI clock begins toggling when the WR strobe goes High.
18-6
RESERVED
R
0x0
5-4
ASIZE
R/W
0x0
Address Bus Size This field defines the size of the address bus.
The address can be up to 4-bits wide with a 24-bit data bus, up to
12-bits wide with a 16-bit data bus, and up to 20-bits wide with an 8-
bit data bus. If the full address bus is not used, use the least
significant address bits.
Any unused address bits can be used as GPIOs by clearing the
AFSEL bit for the corresponding GPIOs.
0x0 = No address
0x1 = Up to 4 bits wide.
0x2 = Up to 12 bits wide. This size cannot be used with 24-bit data.
0x3 = Up to 20 bits wide. This size cannot be used with data sizes
other than 8.
3-2
RESERVED
R
0x0
1-0
DSIZE
R/W
0x0
Size of Data Bus This field defines the size of the data bus (starting
at EPI0S0).
Subsets of these numbers can be created by clearing the AFSEL bit
for the corresponding GPIOs.
Size 32 may not be used with clock, frame, address, or other control.
0x0 = 8 bits wide (EPI0S0 to EPI0S7)
0x1 = 16 bits wide (EPI0S0 to EPI0S15)
0x2 = 24 bits wide (EPI0S0 to EPI0S23)
0x3 = 32 bits wide (EPI0S0 to EPI0S31)This size may not be used
with an EPI clock. This value is normally used for acquisition input
and actuator control as well as other general-purpose uses that
require 32 bits per direction.















































