Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 490 of 1141
S
DATA
8
n
DATA
1
1
m
P
1
Transfer bit count
(n = 1 to 8)
Transfer frame count
(m = 1 or above)
FS = 1 and FSX = 1
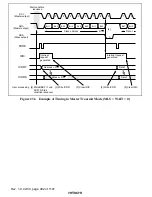
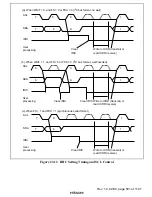
Figure 23.4 I
2
C Bus Data Format (Serial Format)
SDA
SCL
S
SLA
R/
A
9
8
1-7
9
8
1-7
9
8
1-7
DATA
A
DATA
A/
P
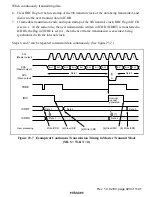
Figure 23.5 I
2
C Bus Timing
Table 23.4
I
2
C Bus Data Format Symbols
Symbol
Description
S
Start condition. The master device drives SDA from high to low while SCL is hig
SLA
Slave address, by which the master device selects a slave device
R/
:
Indicates the direction of data transfer: from the slave device to the master device
when R/
:
is 1, or from the master device to the slave device when R/
:
is 0
A
Acknowledge. The receiving device (the slave in master transmit mode, or the
master in master receive mode) drives SDA low to acknowledge a transfer
DATA
Transferred data. The bit length is set by bits BC2 to BC0 in ICMR. The MSB-first
or LSB-first format is selected by bit MLS in ICMR
P
Stop condition. The master device drives SDA from low to high while SCL is high
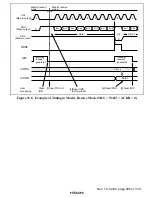
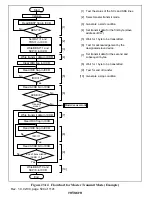
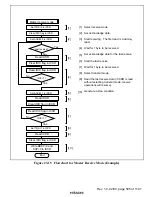
23.3.2
Master Transmit Operation
In master transmit mode, the master device outputs the transmit clock and transmit data, and the
slave device returns an acknowledge signal. The transmit procedure and operations in master
transmit mode are described below.
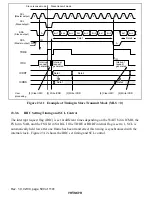
1. Set bit ICE in ICCR to 1. Set bits MLS, WAIT, and CKS2 to CKS0 in ICMR, and bit IICX in
STCR, according to the operating mode.
2. Read the BBSY flag in ICCR, check that the bus is free, then set MST and TRS to 1 in ICCR
to select master transmit mode. After that, write 1 in BBSY and 0 in SCP. This generates a
start condition by causing a high-to-low transition of SDA while SCL is high. As a result, the