Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 88 of 1141
5.1.2
Exception Handling Operation
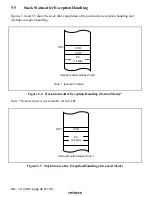
Exceptions originate from various sources. Trap instructions and interrupts are handled as
follows:
1. The program counter (PC) and condition-code register (CCR) are pushed onto the stack.
2. The interrupt mask bits are updated. The T bit is cleared to 0.
3. A vector address corresponding to the exception source is generated, and program execution
starts from that address.
For a reset exception, steps 2 and 3 above are carried out.
5.1.3
Exception Sources and Vector Table
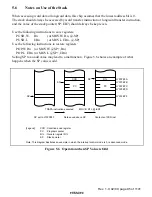
The exception sources are classified as shown in figure 5.1. Different vector addresses are
assigned to different exception sources.
Table 5.2 lists the exception sources and their vector addresses.
Exception sources
• Reset
• Interrupts
• Trap instruction
Note:
*
In this LSI, the watchdog timer generates NMIs.
• Trace (cannot be used in this LSI)
• Direct transition
External interrupts NMI
*
, IRQ5 to IRQ0
Internal interrupts Interrupt sources in on-chip supporting modules
…
…
Figure 5.1 Exception Sources