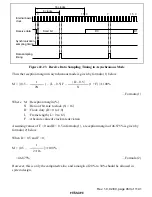
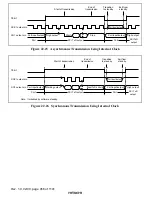
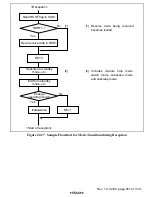
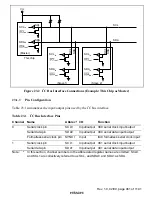
Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 464 of 1141
ICDR is an 8-bit readable/writable register that is used as a transmit data register when
transmitting and a receive data register when receiving. ICDR is divided internally into a shift
register (ICDRS), receive buffer (ICDRR), and transmit buffer (ICDRT). ICDRS cannot be read
or written by the CPU, ICDRR is read-only, and ICDRT is write-only. Data transfers among the
three registers are performed automatically in coordination with changes in the bus state, and
affect the status of internal flags such as TDRE and RDRF.
If IIC is in transmit mode and the next data is in ICDRT (the TDRE flag is 0) following
transmission/reception of one frame of data using ICDRS, data is transferred automatically from
ICDRT to ICDRS. If IIC is in receive mode and no previous data remains in ICDRR (the RDRF
flag is 0) following transmission/reception of one frame of data using ICDRS, data is transferred
automatically from ICDRS to ICDRR.
If the number of bits in a frame, excluding the acknowledge bit, is less than 8, transmit data and
receive data are stored differently. Transmit data should be written justified toward the MSB side
when MLS = 0, and toward the LSB side when MLS = 1. Receive data bits read from the LSB
side should be treated as valid when MLS = 0, and bits read from the MSB side when MLS = 1.
ICDR is assigned to the same address as SARX, and can be written and read only when the ICE
bit is set to 1 in ICCR.
The value of ICDR is undefined after a reset.
The TDRE and RDRF flags are set and cleared under the conditions shown below. Setting the
TDRE and RDRF flags affects the status of the interrupt flags.