Functions
6-207
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
Configuration of
the Automatic
Reclosure Function
This configuration concerns the interaction between the protection and supplementary
functions of the device and the automatic reclosure function. The selection of functions
of the device which are to start the automatic reclosure circuit and which are not to, is
made here.
In the 7SA6 this concerns:
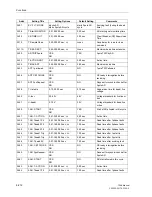
Address
3420
AR w/ DIST.
, i.e. with distance protection,
Address
3421
AR w/ SOTF-O/C
, i.e. with high–current fast tripping,
Address
3422
AR w/ W/I
, i.e. with weak-infeed trip function,
Address
3423
AR w/ EF-O/C
, i.e. with transfer trip and remote trip,
Address
3424
AR w/ DTT
, i.e. with externally coupled trip command,
Address
3425
AR w/ BackUpO/C
, i.e. with time-overcurrent protection.
For the functions which are to start the automatic reclosure, the corresponding ad-
dress is set to
Yes
, for the others to
No
. The other functions (overvoltage protection,
overload protection) cannot start the automatic reclosure because reclosure is of no
use here.
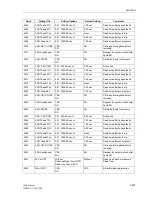
Forced Three-pole
Trip
If reclosure is blocked during the dead time of a single-pole cycle without a three-pole
trip command having been given, the line remains interrupted single-pole. With ad-
dress
3430
AR TRIP 3pole
it is possible to determine that the tripping logic of the
device issues a three-pole trip command in this case (pole discrepancy prevention for
the CB poles). Set this address to
Yes
if the CB can be tripped single-pole and has no
pole discrepancy protection itself. Nevertheless, the device pre-empts the pole dis-
crepancy protection of the CB poles because the forced three-pole trip of the device
is immediately activated as soon as the reclosure is blocked following a single-pole
trip or if the CB auxiliary contacts indicate a non plausible switching state (see also
section 6.14.1 under subtitle “Processing the Circuit Breaker Auxiliary Contacts”). The
forced three-pole trip is also activated when only three-pole cycles are allowed but a
single-pole trip is signalled externally via a binary input.
The forced three pole trip is unnecessary if only a common three-pole control of the
CB is possible.
Dead Line Check/
Reduced Dead
Time
Under address
3431
the dead line check or the reduced dead time function can be
activated. Either the one or the other can be used as the two options are contradictory.
The voltage transformers must be connected to the line side of the circuit breaker if
either of these modes is to be used. If this is not the case or if neither of the two func-
tions is used, set
DLC or RDT
=
WITHOUT
. If the adaptive dead time is used (see
below), the parameters mentioned here are omitted because the adaptive dead time
implies the properties of the reduced dead time.
DLC or RDT
=
DLC
means that the dead line check of the line voltage is used. This
only enables reclosure after it becomes apparent that the line has been dead. In this
case, the setting
U-dead<
under address
3441
determines the limit voltage, phase–
earth,below which the line is considered to be definitely dead (disconnected). The set-
ting is applied in Volts secondary. This value can be entered as a primary value when
parametrizing with a PC and DIGSI
®
4. Address
3438 T U-stable
determines the
measuring time available for determining the no-voltage condition. Address
3440
is
irrelevant here.
DLC or RDT
=
RDT
means that the reduced dead time is used. This is described in
detail in section 6.14.1 under subtitle “Reduced Dead Time (RDT)”, page 196. In this
case the setting under address
3440
U-live>
determines the limit voltage, phase–
earth,above which the line is considered to be fault-free. It must be set smaller than
the smallest expected operating voltage. The setting is applied in Volts secondary.
This value can be entered as a primary value when parametrizing with a PC and
DIGSI
®
4. Address
3438
T U-stable
determines the measuring time available for
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA6
Page 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Page 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...