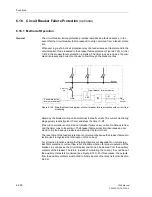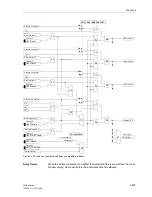
Functions
6-262
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
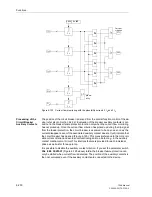
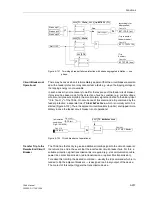
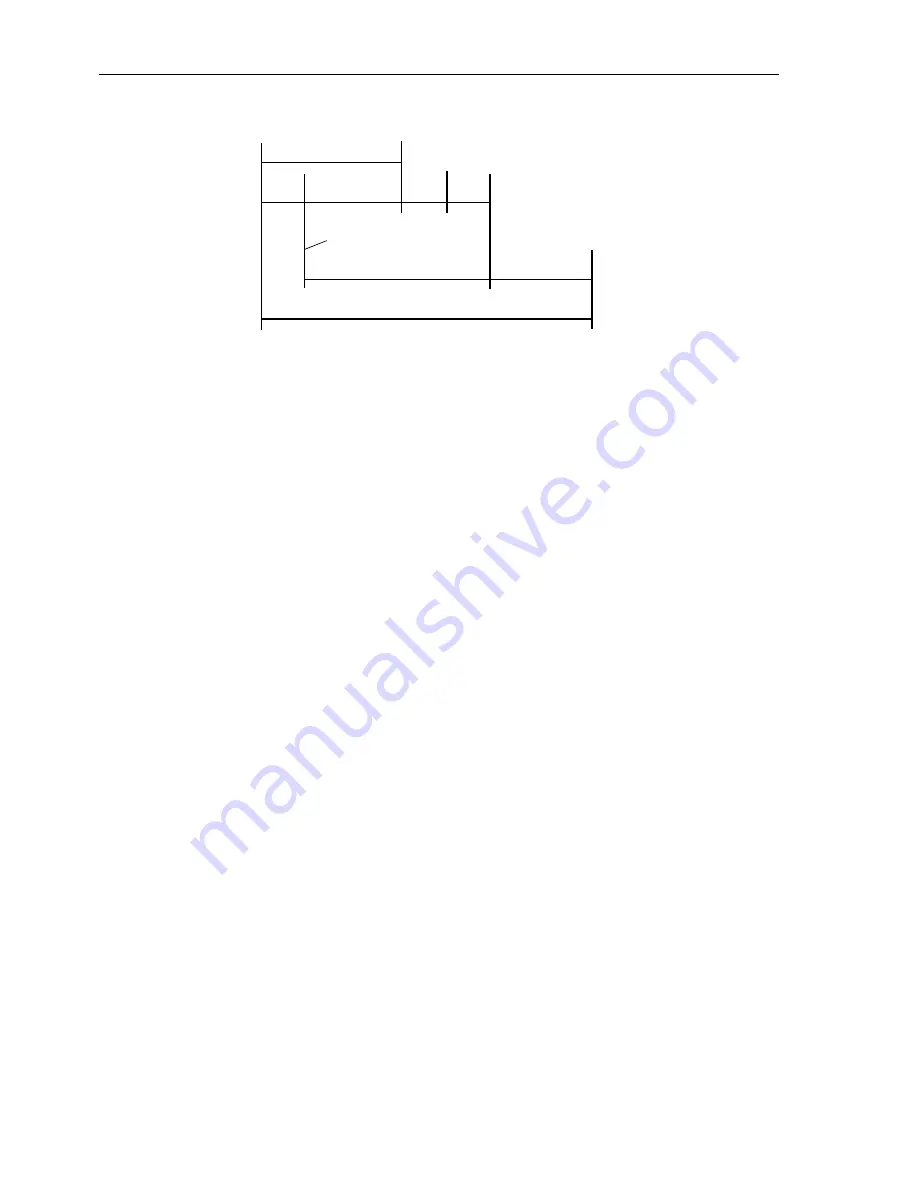
Figure 6-137 Time sequence example for normal clearance of a fault, and with circuit breaker
failure, using single-stage breaker failure protection
Circuit Breaker not
Operational
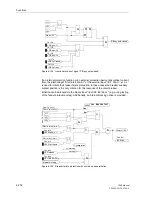
If the circuit breaker associated with the feeder is not operational (e.g. control voltage
failure or air pressure failure), it is apparent that the local breaker cannot clear the
fault. Time delay before tripping the adjacent breakers is not necessary in this case. If
the relay is informed about this disturbance (via the binary input “
>CB faulty
”, the
adjacent circuit breakers (bus-bar and remote end if applicable) are tripped after the
time
T3-BkrDefective
(address
3907
) which is usually set to
0
.
Address
3908
Trip BkrDefect.
determines to which output the trip command is
routed in the event that the breaker is not operational when a feeder protection trip oc-
curs. Select that output which is used to trip the adjacent breakers (bus-bar trip).
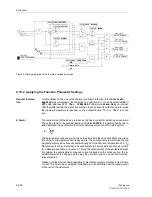
End Fault Protec-
tion
The end fault protection can be switched
On
or
Off
separately under address
3921
End Flt. stage
. An end fault is a short-circuit between the circuit breaker and the
current transformer set of the feeder. The end fault protection presumes that the de-
vice is informed about the circuit breaker position via breaker auxiliary contacts con-
nected to binary inputs.
If, during an end fault, the circuit breaker is tripped by a reverse fault stage of the feed-
er protection or by the bus-bar protection (the fault is a bus-bar fault as determined
from the location of the current transformers), the fault current will continue to flow, be-
cause the fault is fed from the remote end of the feeder circuit.
The time
T-EndFault
(address
3922
) is started when, during the fault detection con-
dition of the feeder protection, the circuit breaker auxiliary contacts indicate open
poles and, at the same time, current flow is detected (address
3902
). The trip com-
mand of the end fault protection is intended for the transmission of an intertrip signal
to the remote end circuit breaker.
Thus, the delay time must be set such that it can bridge out short transient apparent
end fault conditions which may occur during switching of the breaker.
Pole Discrepancy
Supervision
The pole discrepancy supervision can be switched
On
or
Off
separately under ad-
dress
3931
PoleDiscrepancy
. It is only useful if the breaker poles can be operated
individually. It avoids that only one or two poles of the local breaker are open continu-
ously. It has to be provided that either the auxiliary contacts of each pole or the series
connection of the NO auxiliary contacts and the series connection of the NC auxiliary
contacts are connected to the device’s binary inputs. If these conditions are not ful-
filled, switch the pole discrepancy supervision
Off
.
Fault inception
Fault clearance time normal
Prot.
trip
CB operating time
Reset
I> BF
Safety
margin
CB–operating time
(adjacent CBs)
Initiation breaker
failure protection
Time delay T2 of breaker
failure protection
Total fault clearance time with breaker failure
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA6
Page 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Page 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...