Functions
6-106
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
6.6.1.7
Blocking scheme
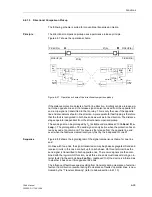
The following scheme is suited for conventional transmission media.
Principle
The blocking scheme uses the transmission channel to send a block signal from one
line end to the other. The signal is sent as soon as the protection function has detected
a fault in reverse direction, optionally also directly after fault inception (jump detector
via the dashed line in Figure 6-62). It is stopped, as soon as the distance protection
detects a fault in the forward direction, alternatively the signal is only sent when the
distance protection detects the fault in the reverse direction. The signal will be main-
tained if the fault is in reverse direction. If the signal is sent with jump detection (i.e.
4060
DisJumpBlocking
routed in parallel with
4056
-
4059
) only a short delay to
allow for signal transmission is required before Z1b trips. A trip can be achieved with
this scheme even if no signal reaches the opposite end. It is therefore mainly used on
long lines, when the signal must be transmitted via the protected line with power line
carrier (PLC), and the attenuation of the transmitted signal could be so severe at the
fault location, that reception at the other line end cannot necessarily be guaranteed.
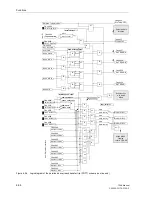
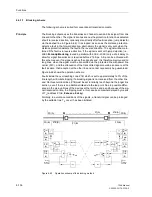
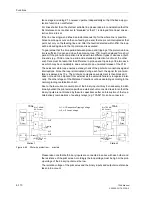
Figure 6-62 shows the operation scheme.
Faults inside the overreaching zone Z1B, which is set to approximately 120% of the
line length, will initiate tripping if a blocking signal is not received from the other line
end. On three terminal lines, Z1B must be set to reliably reach beyond the longer line
section, even if there is an additional infeed via the tee point. Due to possible differ-
ences in the pick-up times of the devices at the two line ends, and because of the sig-
nal transmission time, the tripping must in this case be somewhat delayed by means
of T
V
(address
2108
,
Release Delay
).
Similarly, to avoid race conditions of the signals, a transmit signal can be prolonged
by the settable time T
S
once it has been initiated.
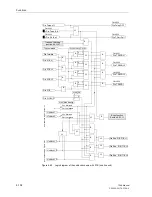
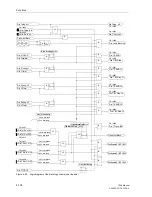
Figure 6-62
Operation scheme of the blocking method
A
B
Z1(A)
Z1(B)
Z1B(A)
Z1B(B)
Z1B
T1B
≥
1
trip
rec.
further
zones
&
Z1 or
d
dt
40 ms
Forw.
(A)
T
S
&
≥
1
transm.
(u,i)
FD
(A)
(A)
T
V
≥
1
trip
rec.
further
zones
&
Z1 or
d
dt
40 ms
Forw.
(B)
T
S
&
≥
1
transm.
(u,i)
FD
(B)
(B)
T
V
FD (A)
FD (B)
FD(A)
FD(B)
(A)
Z1B
T1B
(B)
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA6
Page 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Page 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...