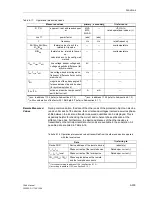
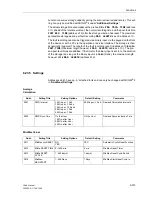
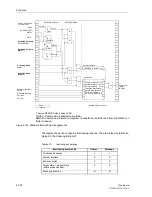
Functions
6-318
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
6.24
Processing of Commands
General
In addition to the protective functions described so far, a control command process is
integrated in the SIPROTEC
®
7SA6 to coordinate the operation of circuit breakers and
other equipment in the power system. Control commands can originate from four com-
mand sources:
−
Local operation using the keypad on the local user interface of the device
−
Local or remote operation using DIGSI
®
4
−
Remote operation via system interface IEC (e.g. SICAM)
−
Automatic functions (e.g. using a binary input)
The number of switchgear devices that can be controlled is basically limited by the
number of available and required binary inputs and outputs. For the output of control
commands it has be ensured that all the required binary inputs and outputs are con-
figured and provided with the correct properties (see also Subsection 5.2.3 under “Bi-
nary outputs for switchgear”).
If specific interlocking conditions are needed for the execution of commands, the user
can program the device with bay interlocking by means of the user-defined logic func-
tions (CFC) (see Section 5.3).
6.24.1 Types of commands
Two types of commands can be issued with this device:
−
Control commands
−
Internal / pseudo commands
Control Commands
These commands operate binary outputs and change the power system status:
−
Commands for the operation of circuit breakers (asynchronous; the synchro-check
can be implemented via CFC by applying the synchronism check and closing con-
trol function) as well as commands for the control of isolators and earth switches,
−
Step commands, e.g. for raising and lowering transformer taps
−
Tap change commands with configurable time settings (Petersen coils)
Internal / Pseudo
Commands
These commands do not directly operate binary outputs. They serve to initiate internal
functions, simulate or acknowledge changes of state.
−
Manual entry execution to change the feedback indication of plant such as the sta-
tus and switching condition, for example in the case of the physical connection to
the auxiliary contacts is not available. A manual entry execution is captured and can
be diplayed accordingly.
−
Additionally, tagging commands can be issued to establish internal settings, such
as switching authority (remote / local), parameter set changeover, data transmis-
sion inhibit and metering counter reset or initialization.
−
Acknowledgment and resetting commands for setting and resetting internal buffers.
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA6
Page 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Page 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...