Functions
6-19
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
Resistance ratio:
Reactance ratio:
Whereby the following applies
R
0
— Zero sequence resistance of the line
X
0
— Zero sequence reactance of the line
R
1
— Positive sequence resistance of the line
X
1
— Positive sequence reactance of the line
These values may either apply to the entire line length or be based on a per unit of line
length, as the quotient is independent of length. Furthermore it makes no difference if
the quotients are calculated with primary or secondary values.
Calculation example:
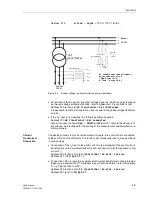
110 kV overhead line 150 mm
2
with the following data
R
1
/s = 0.19
Ω
/km
X
1
/s = 0.42
Ω
/km
Positive sequence impedance
R
0
/s = 0.53
Ω
/km
X
0
/s = 1.19
Ω
/km
Zero sequence impedance
(where s = line length)
The following results are obtained for the earth impedance ratio:
The earth impedance (residual) matching factor setting for the first zone Z1 may be
different from that of the remaining zones of the distance protection. This allows the
setting of the exact values for the protected line, while at the same time the setting for
the back-up zones may be a close approximation even when the following lines have
substantially different earth impedance ratios (e.g. cable after an overhead line). Ac-
cordingly, the settings for the address
1116
RE/RL(Z1)
and
1117
XE/XL(Z1)
are
determined with the data of the protected line while the addresses
1118
RE/
RL(Z1B...Z5)
and
1119
XE/XL(Z1B...Z5)
apply to the remaining zones Z1B
and Z2 up to Z5 (as seen from the relay location).
Earth Impedance
(Residual)
Compensation with
Magnitude and
Angle (K
0
–Factor)
When the complex earth impedance (residual) matching factor K
0
is set, the address-
es
1120
to
1123
apply. In this case it is most relevant that the line angle is set cor-
rectly (cf Address
1105
, see paragraph “General Line Data”, page 17) as the device
needs the line angle to calculate the matching components from the K
0
–factor. These
factors are defined with their magnitude and angle which may be calculated with the
line data using the following equation:
Whereby the following applies
Z
0
— (complex) zero sequence impedance of the line
Z
1
— (complex) positive sequence impedance of the line
R
E
R
L
-------
1
3
---
R
0
R
1
-------
1
–
è
ø
æ
ö
⋅
=
X
E
X
L
-------
1
3
---
X
0
X
1
------
1
–
è
ø
æ
ö
⋅
=
R
E
R
L
-------
1
3
---
R
0
R
1
-------
1
–
è
ø
æ
ö
⋅
1
3
---
0.53
Ω
/km
0.19
Ω
/km
-----------------------------
1
–
è
ø
æ
ö
0.60
=
⋅
=
=
X
E
X
L
-------
1
3
---
X
0
X
1
------
1
–
è
ø
æ
ö
⋅
1
3
---
1.19
Ω
/km
0.42
Ω
/km
-----------------------------
1
–
è
ø
æ
ö
0.61
=
⋅
=
=
K
0
Z
E
Z
L
-------
1
3
---
Z
0
Z
1
------
1
–
è
ø
ç
÷
æ
ö
⋅
=
=
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA6
Page 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Page 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Page 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...