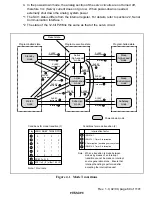
Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 58 of 1141
2.8.5
Power-Down State
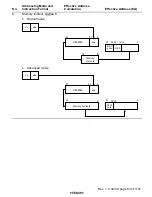
The power-down state includes both modes in which the CPU stops operating and modes in which
the CPU does not stop. There are five modes in which the CPU stops operating: sleep mode,
standby mode, subsleep mode, and watch mode. There are also three other power-down modes:
medium-speed mode, module stop mode, and subactive mode. In medium-speed mode, the CPU
operates on a medium-speed clock. Module stop mode permits halting of the operation of
individual modules, other than the CPU. Subactive mode, subsleep mode, and watch mode are
power-down modes that use subclock input. For details, see section 4, Power-Down State.
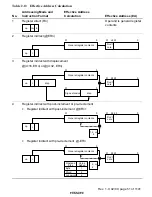
(1) Sleep Mode
A transition to sleep mode is made if the SLEEP instruction is executed while the software
standby bit (SSBY) in the standby control register (SBYCR) and the LSON bit in the low-
power control register (LPWRCR) are both cleared to 0. In sleep mode, CPU operations stop
immediately after execution of the SLEEP instruction. The contents of CPU registers are
retained.
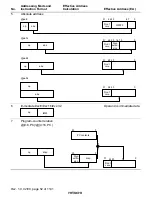
(2) Standby Mode
A transition to standby mode is made if the SLEEP instruction is executed while the SSBY bit
in SBYCR is set to 1 and the LSON bit in LPWRCR and the TMA3 bit in the TMA (timer A)
are both cleared to 0. In standby mode, the CPU and clock halt and all MCU operations stop.
As long as a specified voltage is supplied, the contents of CPU registers and on-chip RAM are
retained.