Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 45 of 1141
2.6.4
Basic Instruction Formats
The CPU instructions consist of 2-byte (1-word) units. An instruction consists of an operation
field (op field), a register field (r field), an effective address extension (EA field), and a condition
field (cc).
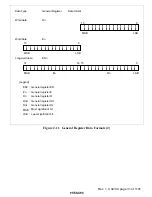
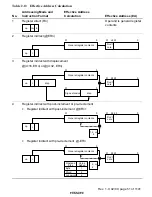
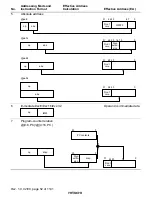
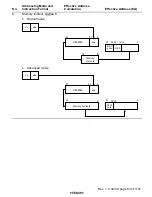
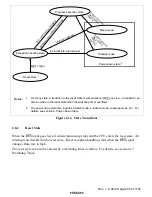
Figure 2.13 shows examples of instruction formats.
op
op
r n
r m
NOP, RTS, etc.
ADD.B Rn, Rm, etc.
MOV.B@(d:16, Rn), Rm, etc.
(1) Operation field only
(2) Operation field and register fields
(3) Operation field, register fields, and effective address extension
r n
r m
op
EA (disp)
(4) Operation field, effective address extension, and condition field
op
cc
EA (disp)
BRA d:16, etc.
Figure 2.13 Instruction Formats (Examples)
(1) Operation Field
Indicates the function of the instruction, the addressing mode, and the operation to be carried
out on the operand. The operation field always includes the first four bits of the instruction.
Some instructions have two operation fields.
(2) Register Field
Specifies a general register. Address registers are specified by 3 bits, data registers by 3 bits or
4 bits. Some instructions have two register fields. Some have no register field.
(3) Effective Address Extension
Eight, 16, or 32 bits specifying immediate data, an absolute address, or a displacement.
(4) Condition Field
Specifies the branching condition of Bcc instructions.