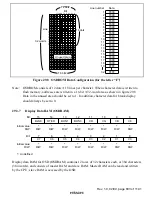
Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 824 of 1141
29.1.5
TV Formats and Display Modes
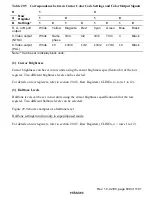
Table 29.3 indicates support for different TV formats in each display mode. Operation is not
guaranteed if a frequency resulting from division by 4 or 2 from the 4fsc/2fsc input pin is not one
of those listed in table 29.3.
Table 29.3
TV Formats and Display Modes
TV Format
fsc (MHz)
Text Display
Superimposed Mode
M/NTSC
3.579545
8 colors
Supported
4.43-NTSC
4.43361875
8 colors
Supported
M/PAL
3.57561149
8 colors
Supported
N/PAL
3.58205625
8 colors
Supported
B.G.H/PAL, I/PAL,
D.K/PAL
4.43361875
8 colors
Supported
SECAM
4.43361875
White/black
Supported
29.2
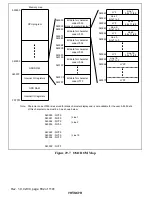
Description of Display Functions
29.2.1
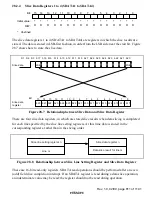
Superimposed Mode and Text Display Mode
There are two types of OSD display: superimposed and text display.
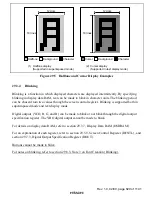
(1) Superimposed Mode
In superimposed mode, the state of operation of a VCR, the current time, and other text and
graphics are displayed on an ordinary TV image. In doing so, there is no mixing of the background
image and the display character colors. There is an internal AFC circuit, enabling reliable text
display. In addition, a halftone function, in which the brightness and chroma saturation of the
background screen in the character display area is reduced to make characters appear to “float”
above the background, is also available. Other features include a character border function.
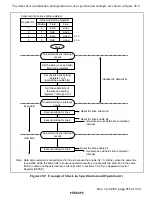
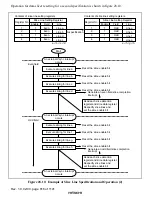
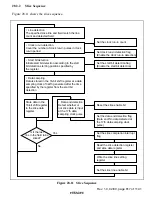
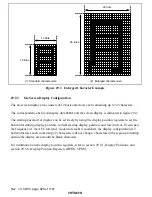
(2) Text Display Mode
In text display mode, characters and graphic data can be displayed in synchronous with the
internal sync signal generated by the internal Csync generator circuit in the sync separator. The
background color for display can be selected from among eight hues. There are plentiful
ornamental functions, including functions for displaying cursors and buttons; cursor and text
colors can be selected from among eight hues, making this function ideal for use in programming
VCR recording and setting modes.