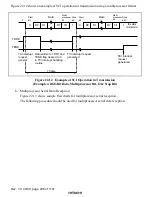
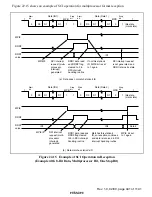
Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 433 of 1141
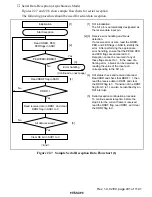
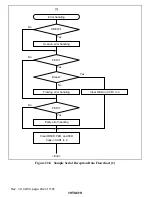
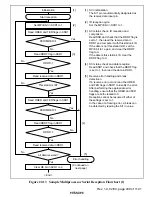
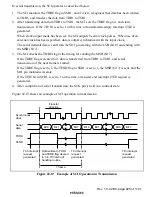
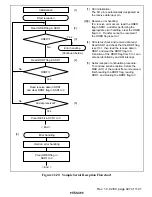
In serial reception, the SCI operates as described below.
1. The SCI monitors the transmission line, and if a 0 stop bit is detected, performs internal
synchronization and starts reception.
2. The received data is stored in RSR1 in LSB-to-MSB order.
3. The parity bit and stop bit are received.
After receiving these bits, the SCI carries out the following checks.
a. Parity check:
The SCI checks whether the number of 1 bits in the receive data agrees with the parity
(even or odd) set in the O/
(
bit in SMR1.
b. Stop bit check:
The SCI checks whether the stop bit is 1.
If there are two stop bits, only the first is checked.
c. Status check:
The SCI checks whether the RDRF flag is 0, indicating that the receive data can be
transferred from RSR1 to RDR1.
If all the above checks are passed, the RDRF flag is set to 1, and the receive data is stored
in RDR1.
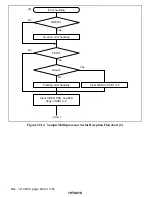
If a receive error* is detected in the error check, the operation is as shown in table 22.11.
Note: *
Subsequent receive operations cannot be performed when a receive error has occurred.
Also note that the RDRF flag is not set to 1 in reception, and so the error flags must be
cleared to 0.
4. If the RIE bit in SCR1 is set to 1 when the RDRF flag changes to 1, a receive-data-full
interrupt (RXI) request is generated.
Also, if the RIE bit in SCR1 is set to 1 when the ORER, PER, or FER flag changes to 1, a
receive-error interrupt (ERI) request is generated.
Table 22.11 Receive Errors and Conditions for Occurrence
Receive Error
Abbrev.
Occurrence Condition
Data Transfer
Overrun error
ORER
When the next data reception is
completed while the RDRF flag
in SSR1 is set to 1
Receive data is not transferred
from RSR1 to RDR1
Framing error
FER
When the stop bit is 0
Receive data is transferred from
RSR1 to RDR1
Parity error
PER
When the received data differs
from the parity (even or odd) set
in SMR1
Receive data is transferred from
RSR1 to RDR1