Rev. 1.0, 02/00, page 517 of 1141
24.2
Register Descriptions
24.2.1
Software-Triggered A/D Result Register (ADR)
ADRH
ADRL
1
0
3
2
5
4
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
7
0
R
6
0
R
9
0
R
8
0
R
11
0
R
10
0
R
0
R
0
R
0
R
ADR9 ADR8 ADR7 ADR6 ADR5 ADR4 ADR3 ADR2 ADR1 ADR0
0
R
12
13
14
15
0
0
0
0
0
0
Bit :
Initial value :
R/W :
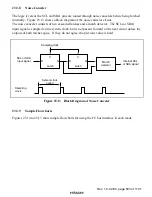
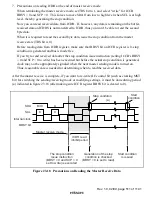
The software-triggered A/D result register (ADR) is a register that stores the result of an A/D
conversion started by software.
The A/D-converted data is 10-bit data. Upon completion of software-triggered A/D conversion,
the 10-bit result data is transferred to ADR and the data is retained until the next software-
triggered A/D conversion completion. The upper 8 bits of the data are stored in the upper bytes
(bits 15 to 8) of ADR, and the lower 2 bits are stored in the lower bytes (bits 7 and 6). Bits 5 to 0
are always read as 0.
ADR can be read by the CPU at any time, but the ADR value during A/D conversion is not fixed.
The upper bytes can always be read directly, but the data in the lower bytes is transferred via a
temporary register (TEMP). For details, see section 24.3, Interface to Bus Master.
ADR is a 16-bit read-only register which is initialized to H'0000 at a reset, and in module stop
mode, standby mode, watch mode, subactive mode and subsleep mode.
24.2.2
Hardware-Triggered A/D Result Register (AHR)
AHRH
AHRL
1
0
3
2
5
4
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
7
0
R
6
0
R
9
0
R
8
0
R
11
0
R
10
0
R
0
R
0
R
0
R
AHR9 AHR8 AHR7 AHR6 AHR5 AHR4 AHR3 AHR2 AHR1 AHR0
0
R
12
13
14
15
0
0
0
0
0
0
Bit :
Initial value :
R/W :
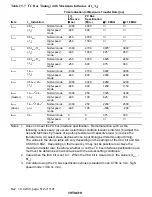
The hardware-triggered A/D result register (AHR) is a register that stores the result of an A/D
conversion started by hardware (internal signal: ADTRG and DFG) or by external trigger input
(
$'75*
).
The A/D-converted data is 10-bit data. Upon completion of hardware- or external-triggered A/D
conversion, the 10-bit result data is transferred to AHR and the data is retained until the next
hardware- or external- triggered A/D conversion completion. The upper 8 bits of the data are
stored in the upper bytes (bits 15 to 8) of AHR, and the lower 2 bits are stored in the lower bytes
(bits 7 and 6). Bits 5 to 0 are always read as 0.