37
Commands Listed According to Purpose
Section 1-8
1-8
Commands Listed According to Purpose
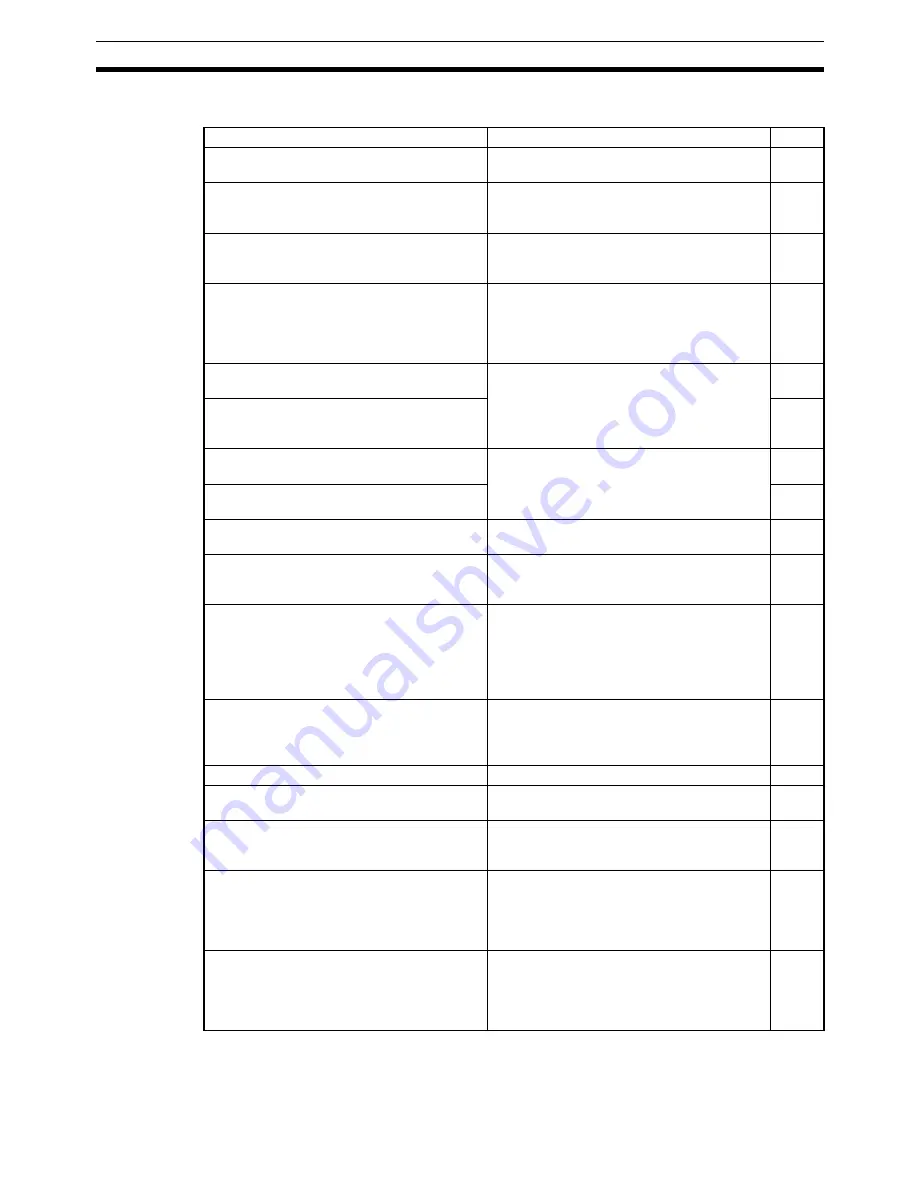
Purpose
Command/Function
Page
To speed up winding operations.
TRAVERSE (G32)
336,
412
To speed up pick-and-place operations (by
starting the next operation without waiting for
positioning to be completed).
Use IN-POSITION CHECK OFF MODE
(G13).
342,
399
To use multiturn circular interpolation or heli-
cal circular interpolation (for winding machine
operations, etc.).
CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION
(CLOCKWISE) or CIRCULAR INTERPOLA-
TION (COUNTERCLOCKWISE) (G02/G03)
331,
388
To start a CPU Unit interrupt task when
positioning is completed or when passing
through a specified position (with high-speed
synchronization between the ladder diagram
program and the MC Unit).
Interrupt notification (D code output)
348,
438
To control an axis in a fixed direction (for a
turntable or fixed-direction conveyer).
Unlimited feeding function
370
To refresh the present position in a 360
°
range, for example, during unlimited feeding
(remembering the number of turns).
370
To speed up feeding for axes using the MPG
(Manual Pulse Generator).
Electronic gear function:
Multiplication of numerator and denominator
for MPG/sync encoder, and electronic gear
function ON/OFF switch
365
To synchronize axis feeding with a device
such as a conveyer.
365
During interrupt feeding, to execute position-
ing even when no interrupt signal is input.
INTERRUPT FEEDING (G31).
334,
406
To change speeds during operation (during
PTP control, linear interpolation, or circular
interpolation).
Override function
349
After a fixed amount of axis movement during
operation, to notify the CPU Unit of interrupts,
and so on, without stopping operation.
(Improving tack time by controlling an external
device before the operation has been
completed.)
Stopover function (M code or D code output at
a given present position)
279,
299,
346
To perform an origin search to simplify
absolute encoder adjustment operations
(replacing motor, mechanical system belts,
decelerator, etc.).
Absolute encoder system origin search
function
Sec. 9
To shorten the origin search time.
Use origin search pattern 2.
472
To stop smoothly for CW and CCW inputs
during origin search.
Either deceleration stop or accumulated pulse
stop can be selected.
471
To turn the motor, or to stop.
Servo-lock, servo-unlock function
293,
296,
353
To forcibly set the error counter to 0 when no
speed reference is provided to the servo driver
(when a deceleration reference has
finished being output). Example: molding
machine press control.
Error counter reset function
284,
351
To change servo system parameters
(acceleration deceleration time, position loop
gain, in-position, etc.) during operation. Exam-
ple: Increasing the accuracy of circular inter-
polation with position loop feedback gain.
Changing servo system parameters:
Use CHANGE PARAMETER (G69).
345,
421
Summary of Contents for CS1W-MC221 -
Page 1: ...Motion Control Units Cat No W359 E1 04 CS1W MC221 V1 421 V1 OPERATION MANUAL ...
Page 2: ...CS1W MC221 V1 421 V1 Motion Control Units Operation Manual Revised February 2008 ...
Page 3: ...iv ...
Page 5: ...vi ...
Page 11: ...xii ...
Page 15: ...xvi ...
Page 19: ...xx ...
Page 27: ...xxviii Conformance to EC Directives 6 ...
Page 133: ...106 Installation Section 2 2 2 2 4 Dimensions CS1W MC421 CS1W MC221 ...
Page 173: ...146 Connecting Peripheral Devices Section 2 7 ...
Page 227: ...200 Command Area Section 3 6 ...
Page 351: ...324 Interface Specifics Section 5 4 ...
Page 513: ...486 Absolute Encoder Interface Specifications Section 9 7 ...
Page 575: ...548 Error Log Section 12 6 ...
Page 589: ...562 Performance Appendix A ...
Page 655: ...628 Control Bit Flag Timing Charts Appendix E ...
Page 683: ...656 Origin Search Patterns Appendix F ...
Page 685: ...658 Encoder Divider Rate and Rotation Speed for OMRON Servo Drivers Appendix G ...
















































