SD710 Series Servo Drive User Manual Chapter 5 Commissioning and Operation
14
!
!
●
For the vertical axis, the workpiece may fall after entering overtravel because the brake signal
(/BK) turns on (brake release). To prevent the workpiece from falling, set the "servo motor to enter the
zero position fixed state after stopping (Pn007=1)".
●
When an external force is applied, the motor will be blocked at the base after stopping when it
enters overtravel, and the load shaft end may be pushed back by the external force. To prevent the
servo motor from being pushed back by an external force, set the "servo motor to zero fixed state after
stopping (Pn007=1)".
●
When the servomotor is stopped or rotating at a very low speed, no braking force will be
generated when the dynamic braking stop is selected, just as in the free-running state.
●
The setting of the zero-speed stop method is valid only for position control and speed control.
5.1.11 Regenerative Brake Setting
When the motor torque and speed are in opposite directions, energy is fed back into the drive from the motor side, causing
the drive bus voltage value to raise, and when the bus voltage rises to the preset braking point, the energy can only be
consumed through the braking resistor. At this point, the braking energy must be required to be consumed, otherwise, it
will cause damage to the drive.
Note
●
When connecting an external regenerative braking resistor, be sure to set the appropriate values for
Pn012 and Pn013, otherwise the regenerative overload alarm will not be detected properly and may
cause damage to the external regenerative resistor.
●
When selecting an external regenerative braking resistor, be sure to confirm that the capacity is
appropriate, as this may result in injury or fire.
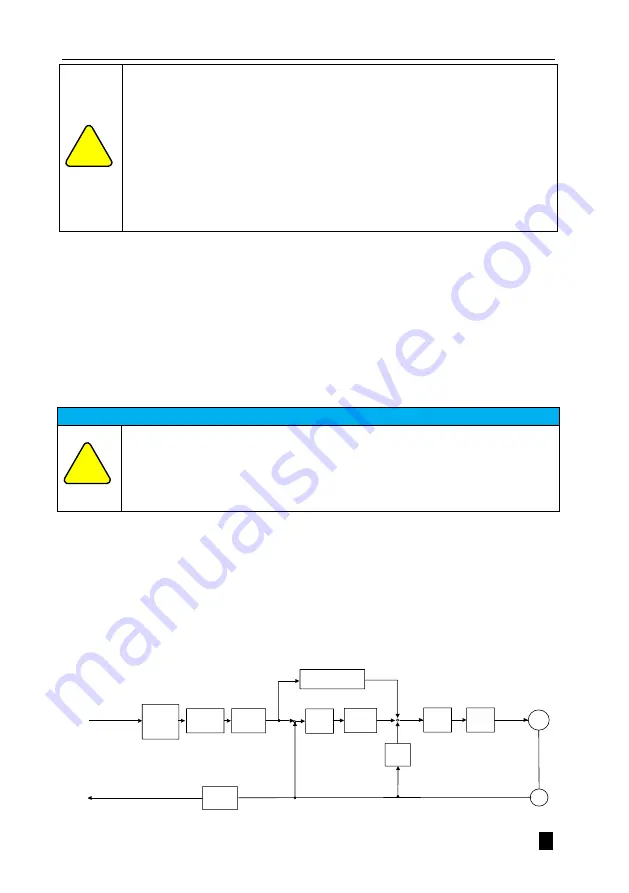
5.2 Location Model
Position control is the control of the position of the motor by position commands. The total number of position commands
is used to determine the target position of the motor and the position command frequency determines the motor rotation
speed. The position command can be given by external pulse input, internal position position command, etc. Through the
internal encoder (the motor comes with an encoder), the servo drive can achieve fast and accurate control of the position
and speed of the machinery.
Position control is mainly used where positioning control is required.
M
Position
command
source and
direction
Electronic
gear ratio
Smooth
filtering
Error
counter
Speed feedforward
Spped
loop
control
ENC
Speed
switch
Frequency
division
Position
command
Encoder
frequency
division output
Position
loop gain
Current
loop
control
-
-
+
+
+
















































