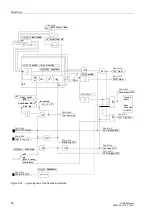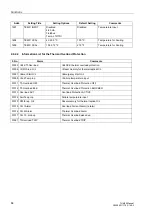
Startup Overcurrent Protection (ANSI 51)
71
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.11
Startup Overcurrent Protection (ANSI 51)
General
Gas turbines can be started by means of a frequency starting converter. A switched-
mode converter feeds a current into the generator and creates a rotating field whose
frequency gradually increases. This causes the rotor to turn and thus to drive the tur-
bine. At approx. 70 % of the rated speed, the turbine is ignited and further accelerated
until it attains rated speed. The startup converter is switched off.
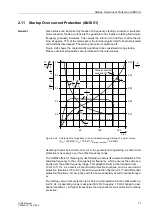
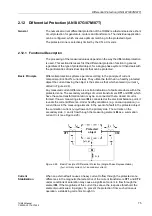
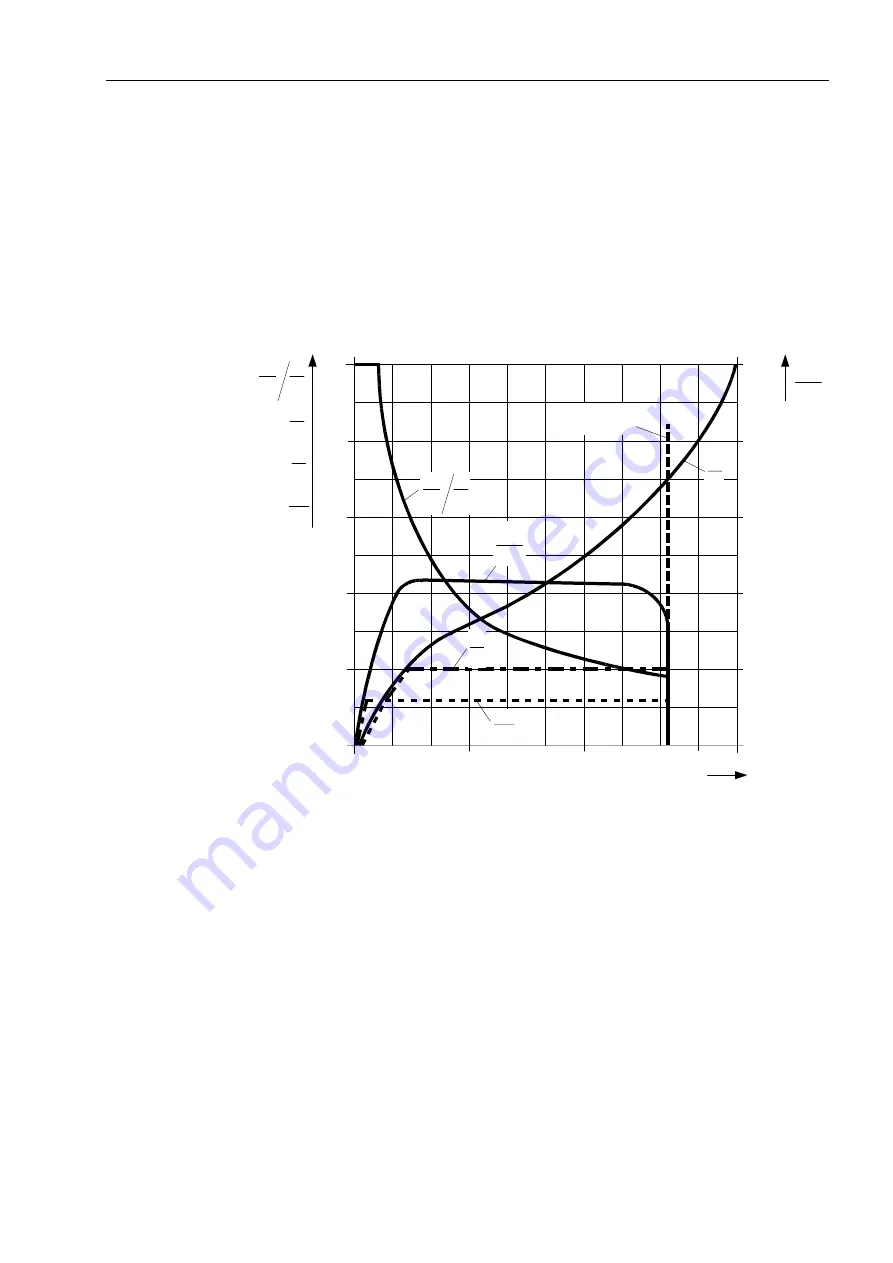
Figure 2-24 shows the characteristic quantities to be considered during startup.
Please note that all quantities are normalized to the rated values.
Figure 2-24 Characteristic Quantities to be Considered during Startup of a Gas Turbine
(S
N
= 150 MVA; U
N
= 10.5 kV; P
Startup converter
= 2.9 MW)
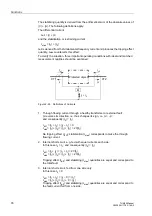
Assuming that a short-circuit can occur in the generator during startup, a short-circuit
protection is necessary over the entire frequency range.
The 7UM62 offers for this a highly useful feature, namely its automatic adaption of the
sampling frequency to the current generator frequency, which ensures the same sen-
sitivity over the entire frequency range. This adaption starts at the transition from
10 Hz to 11 Hz. As a result, all short-circuit protection functions, such as overcurrent
protection (Sections 2.6 to 2.8), impedance protection (Section 2.17) and differential
protection (Section 2.12) are active with the same sensitivity as with nominal frequen-
cy.
The startup overcurrent protection is a short-circuit protection function that works be-
low 10 Hz. Its operating range is designed for 2 Hz to approx. 10 Hz (change to oper-
ational condition 1). At higher frequencies, the above short-circuit protection functions
are active.
60
120
180
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
t (s)
n
n
N
I
I
N
U
U
N
n
n
N
I
I
N
U
U
N
U
U
N
f
f
N
U
U
N
f
f
N
-P
S
N
-P
S
N
Startup converter
switched off