Functions
236
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
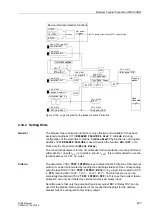
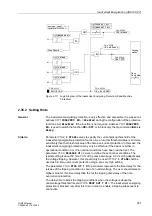
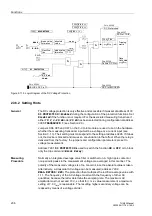
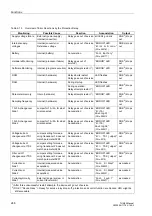
Figure 2-115 Logic Diagram of the DC Voltage Protection
2.36.2 Setting Hints
General
The DC voltage protection is only effective and accessible if it was set at address
=
Enabled
during the configuration of the protection functions. Set
Disabled
if the function is not required. For the associated measuring transducer 1,
either
10 V
,
4–20 mA
oder
20 mA
has been selected during configuration at address
(see Section 2.3).
Jumpers X94, X95 and X67 on the C–I/O–6 module are used to set in the hardware
whether the measuring transducer input will be a voltage or a current input (see
Section 3.1.3). Their setting must correspond to the setting at address
. If it does
not, the device is blocked and issues an annunciation to that effect. When the relay is
delivered from the factory, the jumpers and configuration parameters are set to
voltage measurement.
Address
is used to switch the function
ON
or
OFF
, or to block
only the trip command (
Block Relay
).
Measuring
Procedure
Normally an integrated average value filter is switched on. A high ripple content or
non-periodic peaks in the measurement voltage are averaged in this manner. The
polarity of the measured voltages is of no concern since the absolute value is taken.
Alternatively, a sinusoidal AC voltage can be measured (address
=
RMS
). The protection then multiplies the rectified average value with
1.11. The frequency of the AC voltage must match the frequency of other AC
quantities, because the latter determine the sampling rate. The maximum AC
amplitude must not exceed 10 V, so that for r.m.s. value measurement a maximum
setting of 7.0 V
rms
is reasonable. The resulting higher secondary voltage can be
reduced by means of a voltage divider.
Tripping
matrix
FNo. 05306
mean value
formation
Rectifica-
tion
absolute
value
mean value
formation
factor
1.11
mean
FNo. 05307
&
&
2 mA
4-20 mA
10V
”1”
20 mA
U
=
U
∼
I
=
I
∼
or.
r.m.s.
&
FNo. 05293
FNo. 05302
FNo. 05308
TMin
TRIP CMD
Mean
R.M.S.