Functions
42
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.7
Definite-Time Overcurrent Protection (I>>, ANSI 50, 51, 67)
with Direction Detection
The overcurrent protection is used as backup protection for the short-circuit protection
of the protected object. It also provides backup protection for downstream network
faults which are not promptly disconnected and thus may endanger the protected
object.
The 7UM62 relay allows to choose between the input transformers of side 1 and side
2 for allocation of the overcurrent protection function. This choice is made during
configuration (see Section 2.2).
In order to ensure that pick-up always occurs even with internal faults, the protection
- for generators - is usually connected to the current transformer set in the neutral
leads of the machine (side 2). If this is not the case for an individual power system, the
I>> stage can be combined with a short-circuit direction determination and switch off
a generator short circuit by way of an undelayed tripping; the selectivity is not affected
by this.
Initially, the currents are numerically filtered so that only the fundamental-frequency
currents are used for the measurement. This makes the measurement insensitive to
transient conditions at the inception of a short-circuit and to asymmetrical short-circuit
currents (d.c. component).
2.7.1
Functional Description
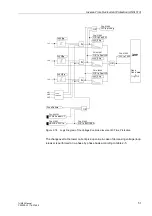
I>> Stage
Each phase-to-phase current of side 1 or 2 (depending on the configuration) is
compared individually with the
common setting value. Currents above these
value are recorded and signalled individually. A trip signal is transmitted to the matrix
as soon as the corresponding
time delays have elapsed. The drop-out value is
± 95 % below the pick-up value.
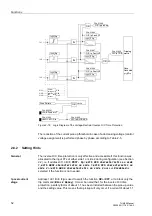
Direction Detection
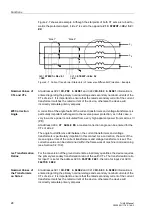
If this protection function has been assigned to the input transformers of side 1, the
I>> stage is equipped with a (disconnectable) direction element permitting a tripping
only for faults in backward (i.e. machine) direction.
For this reason, this stage can be used especially in applications where no current
transformers exist in the generator starpoint and undelayed tripping is nevertheless
required in case of generator faults (see figure 2-11).
Figure 2-11
Selectivity via Short-Circuit Direction Detection
The direction is detected phase-selectively by means of a cross-polarized voltage.
The phase-to-phase voltage located vertical to the vector of the fault current is
G
reverse