Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
217
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.33
Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
General
The rotor temperature of a motor generally remains well below its maximum allowable
temperature during normal operation and even during severe loading conditions.
However, during motor starting, the rotor can heat up quickly. If multiple starting
attempts are made in a short duration of time, the rotor could suffer thermal damage.
Therefore, the 7UM62 motor start blocking feature is available. A motor restart inhibit
signal is initiated when the relay projects rotor temperature exceeds the maximum
allowable temperature, and blocking continues until the calculated rotor temperature
decreases below the reset level. To block starting, the restart inhibit signal must be
masked to an output relay whose contact is inserted in the motor starting circuit.
2.33.1 Functional Description
Determining the
Rotor
Overtemperature
Because the rotor current cannot be measured directly, the stator current must be
used to generate a thermal profile of the rotor. The r.m.s. values of the currents are
generated for this. The excessive rotor temperature
Θ
R
is calculated using the highest
of the three phase currents. The thermal limit values for the rotor winding are based
on manufacturer’s data regarding the nominal starting current, maximum permissible
starting time, and the number of starts permitted from cold (n
cold
) and warm (n
warm
)
conditions. From this data, the device performs the necessary calculations to establish
the thermal rotor profile and issues a blocking signal until the thermal rotor profile
decreases below the restarting limit.
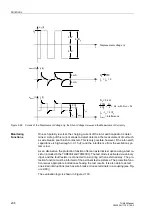
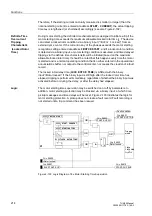
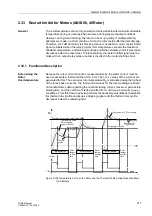
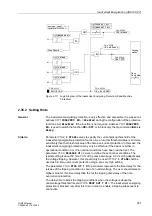
Figure 2-104Temperature Curve at the Rotor and the Thermal Profile during Repeated Start-
Up Attempts
Θ
L
Maximum permissible rotor temperature
Temperature curve:
Rotor cage bar
Rotor cage bar
Thermal
profile
Threshold of restart
Motor started
Rotor
temper.
Motor started
Motor started
t
equilibr.
Cool down at
τ
·
k
τ
at running
1.
Startup
2.
Startup
3.
Startup
t
Current
CB I >
Cool down at
τ
·
k
τ
at stop
upper side limit
lower side limit
time
Rotor
temper.
equilibr.
time
Rotor
temper.
equilibr.
time
inhibit (
Θ
ReInhib)