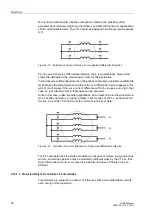
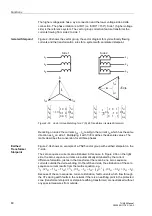
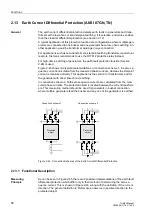
Differential Protection (ANSI 87G/87M/87T)
85
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
Unwanted differential currents may also be cause by parallel connection of
transformers or by transformer overexcitation due to excessive voltage.
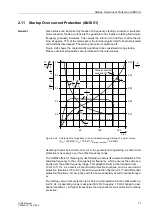
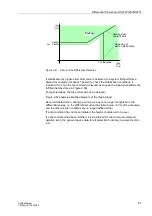
The inrush current can amount to a multiple of the rated current and is characterized
by a considerable 2nd harmonic content (double rated frequency) which is practically
absent in the case of a short-circuit. If the second harmonic content exceeds a select-
able threshold, tripping is blocked.
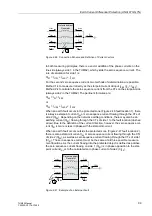
Figure 2-39
Inrush Current – Example
Recording of the Three Higher-Voltage Currents
Besides the second harmonic, another harmonic can be selected in the 7UM62 to
cause blocking. A choice can be made between the third and fifth harmonic as
harmonic stabilization.
Steady-state overexcitation of the transformer is characterized by odd harmonic
content. The third or fifth harmonic is suitable to provide stabilization. But, as the third
harmonic is often eliminated in power transformers (e.g. by the delta winding), the use
of the fifth is more common.
Converter transformers also produce odd harmonic content which is practically absent
in the case of internal short-circuits.
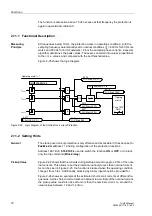
The differential currents are analyzed with regard to their harmonics content.
Numerical filters are used to perform a Fourier analysis of the differential current. As
soon as the harmonics content exceeds the set thresholds, a stabilization of the
respective phase evaluation is started. The filter algorithms are optimized with regard
to their transient behaviour such that additional measures for stabilization during
dynamic conditions are not necessary.
The harmonic stabilization is maintained for two periods after decrease of the
differential current. This prevents an unwanted under-stabilization when external
faults are cleared and the higher-order harmonics disappear.
Since the inrush stabilization operates individually per phase, the protection is fully
operative even when the transformer is switched onto a single-phase fault, while
inrush currents may possibly be present in one of the healthy phases.
In ”modern type” transformers in particular, the 2nd harmonics content may not
exceed the threshold value in all three phases on switch-on. To avoid spurious
tripping, the so-called “crossblock” function must be activated. As soon as an inrush
current is detected in one phase, the other phases of the differential protection stage
IDIFF> are blocked.
The cross-block function can be limited to a selectable duration. After this cross-block
time has elapsed, no more cross-block is possible for as long as a running fault