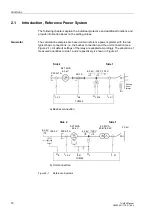
Functions
28
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
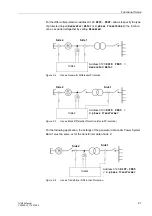
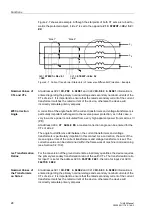
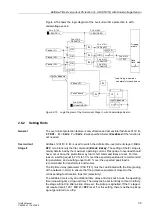
Figure 2-7 shows an example. Although the starpoints of both CT sets are turned to-
wards the protected object, “side 2” is set to the opposite:
=
.
Figure 2-7 Current Transformer Starpoints in Transverse Differential Protection - Example
Nominal Values of
CTs and VTs
At addresses
and
information is
entered regarding the primary nominal voltage and secondary nominal currents of the
CTs of side 1. It is important to ensure that the rated secondary current of the current
transformer matches the rated current of the device, otherwise the device will
incorrectly calculate primary amperes.
W0 Correction
Angle
A correction of the angle faults of the current transformers and voltage transformers is
particularly important with regard to the reverse power protection, as in this case, a
very low active power is calculated from a very high apparent power (for small cos
ϕ
(PF)).
At address
a constant correction angle can be entered for the
CTs of side 2.
The angle fault difference
∆ϕ
between the current transformers and voltage
transformers is particularly important in this context. As a correction, the sum of the
mean angle errors of the current transformers and voltage transformers is set. The
corrective value can be determined within the framework of machine commissioning
(see Section 3.4.10.2).
Iee Transformation
Ratios
For the conversion of the ground currents Iee in primary quantities, the device requires
the primary/secondary transformation ratio of the earth CTs. The transformation ratio
for input 1 is set at the address
, the ratio for input 2 at
.
Nominal Values of
the Transformers
on Side 2
At addresses
and
information is
entered regarding the primary nominal voltage and secondary nominal currents of the
CTs of side 2. It is important to ensure that the rated secondary current of the current
transformer matches the rated current of the device, otherwise the device will
incorrectly calculate primary amperes.
L
1
L
2
L
3
0201
STRPNT–>OBJ S1
=
“Side 1“
“Side 2“
0210
STRPNT–>OBJ S2
=