Threshold Supervision
261
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.40
Threshold Supervision
General
This function monitors the thresholds of selected measured values, checking whether
the values exceed or drop below these thresholds. The processing speed of this func-
tion is so high that it can be used for protection applications. The necessary logical can
be implemented by means of CFC.
The principal field of application of threshold supervision are high-speed supervision
and automatic functions as well as application-specific protection functions (e.g. pow-
er plant decoupling) which are not included in the scope of protection functions.
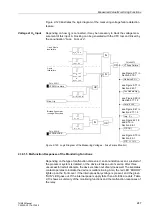
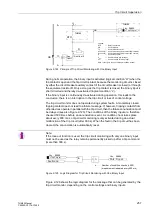
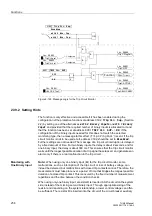
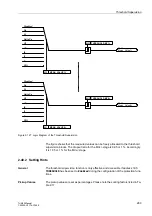
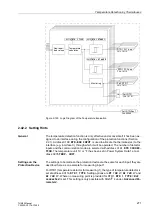
2.40.1 Functional Description
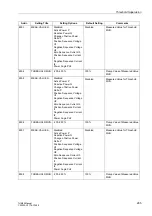
There are 6 threshold supervision blocks, 3 each for responding to values in excess
of and below the threshold. They output as result a logical indication that can be further
processed by the CFC.
A total of 9 processable measured values are available, all of which can be evaluated
as percentages. Each threshold block can be allocated one of these 9 measured val-
ues. As in all other protection functions, the measured values are referred to second-
ary quantities.
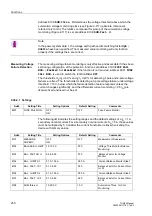
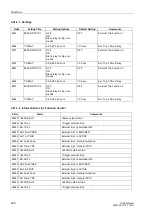
Table 2-17 below show the useable measured values. The threshold values are que-
ried once per cycle.
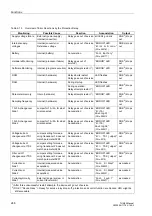
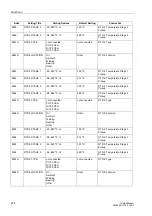
Table 2-17
Measured Values
Measured Value
Scaling
Comments
P
(Active power)
P/S
N,sec
⋅
100 %
(normalized with
addr.
The positive sequence system quantities for U
and I are formed once per cycle from the sampled
values. From the result, P is calculated. The
measuring result is subject to the angle correction
(address
) in the current path.
Q
(Reactive power)
Q/S
N,sec
⋅
100 %
(normalized with
addr.
The positive sequence system quantities for U
and I are formed once per cycle from the sampled
values. From the result, Q is calculated. The
measuring result is subject to the angle correction
(address
) in the current path.
∆
P
(Change of active
power)
∆
P/S
N,sec
⋅
100 %
(normalized with
addr
The active power difference is calculated from the
active power over a measuring window of 3
cycles.
U1
(Positive
sequence voltage)
U1/U
N,sec
⋅
100 %
(normalized with
addr.
The positive sequence voltage is determined
from the phase-to-earth voltages on the basis of
the definition equation for symmetrical
components. The calculation is perfomed once
per cycle.
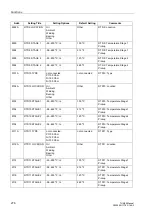
U2
(Negative
sequence voltage)
U2/U
N,sec
⋅
100 %
(normalized with
addr.
The negative sequence voltage is determined
from the phase-to-earth voltages on the basis of
the definition equation for symmetrical
components. The calculation is perfomed once
per cycle.