Functions
142
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
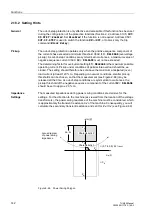
2.18.2 Setting Hints
General
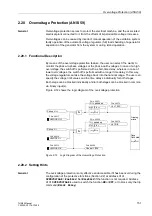
The out-of-step protection is only effective and accessible if this function has been set
during the configuration of the protective functions (Section 2.2, address
=
Enabled
. Set
Disabled
if the function is not required. Address
is used to switch the function
ON
or
OFF
, or to block only the trip
command (
Block Relay
).
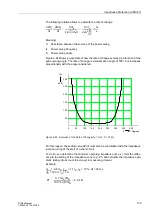
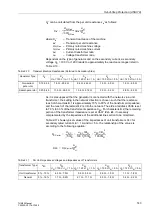
Pickup
The out-of-step protection operates only when the positive sequence component of
the currents has exceeded a minimum threshold
(overvoltage
pickup). As out-of-step conditions are symmetrical occurrences, a maximum value of
negative sequence current
must not be exceeded.
The determining factor for overcurrent setting
is the maximum possible
operating current. Pickup under conditions of permissible overload should be ex-
cluded. The setting should therefore be set above the maximum anticipated (over-)
load current (at least 120 % I
N
. Depending on network conditions, smaller pickup
thresholds can be chosen, so that the measurement (see Figure 2-68) may be
released all the time. As out-of-step conditions are symmetrical occurrences, the
pickup threshold of the negative sequence component of the current
should be set to approx. 20 % I
N
.
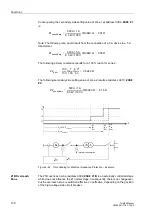
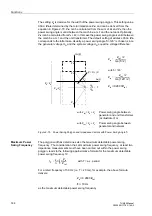
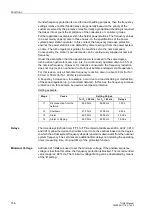
Impedance
Settings
The measured impedances during power swing conditions are decisive for the
settings. For the direction to the machine (as viewed from the location of the voltage
transformers), the power swing reactance of the machine must be considered, which
is approximately the transient reactance X
d
' of the machine. Consequently, you will
calculate the secondary transient reactance and set it for Z
b
≈
X
d
' (see Figure 2-69).
Figure 2-69
Power Swing Polygon
Z
d
–Z
c
Z
c
Z
b
Z
a
Characteristic 2
Z
d
Re(Z
)
Im(Z)
ϕ
P
Characteristic 1
ý
þ
ü
ü
ý
þ
≈
X
d
’
≈
(0.7 to 0.9) Z
K Transf
Locus diagram
of power swing
impedance