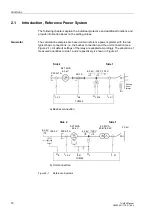
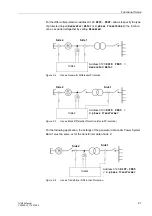
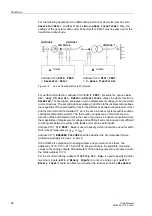
1 Introduction
8
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
Unbalanced Load
Protection
•
Evaluation of negative sequence component of the three phase currents;
•
Alarm stage when a set unbalanced load is exceeded;
•
Thermal replica for rotor temperature rise with adjustable negative sequence factor
K and adjustable time for cool down;
•
High-speed trip stage for large unbalanced loads (can be used for short-circuit
protection).
Startup
Overcurrent
Protection
•
I> stage for lower speed ranges (e.g. startup of generators with frequency starting
converter).
Differential
Protection
Used for generator, motor or transformer differential protection
•
Tripping characteristic with current restraint;
•
High degree of sensitivity;
•
Insensitivity to DC components and current transformer saturation;
•
High degree of stability even with different degrees of CT saturation;
•
Restraint feature against high inrush currents with 2nd harmonics;
•
Restraint feature against transient and steady-state fault currents with 3rd or 5th
harmonics;
•
High-speed tripping in case of high-current faults;
•
Integrated matching of transformer vector group;
•
Integrated matching of transformation ratio with consideration of different c.t. rated
currents.
Earth Current
Differential
Protection
•
Tripping characteristic with restraining current;
•
Variable selection of measured quantities for all normal plant conditions;
•
High sensitivity;
•
Additional stabilisation measures against overfunction at external faults.
Underexcitation
Protection
•
Conductance measurement from positive sequence components;
•
Multi-step characteristic for steady-state and dynamic stability limits;
•
Detection of the excitation voltage.
Reverse Power
Protection
•
Calculation of power from positive sequence components;
•
Highly sensitive active power measurement (detection of small motoring powers
even with small power factor cos
ϕ
, angle error correction);
•
Insensitive to power swings;
•
Independent long-time stage and short-time stage with stop valve tripped.
Forward Power
Supervision
•
Calculation of power from positive sequence components;
•
Supervision of over-power (P>) and/or under-power (P<) with individually
adjustable power limits;
•
Optionally high-speed or high-accuracy power measurement.