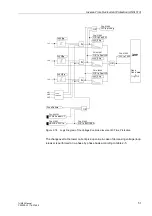
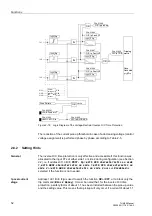
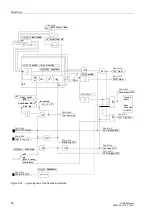
Thermal Overload Protection (ANSI 49)
59
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.9.2
Setting Hints
General
Thermal overload protection is only effective and accessible if address
was set to
Enabled
. Set
Disabled
if the function is not required.
Transformers and generators are prone to damage by overloads which last for an
extended period of time. For this reason, short circuit protection elements such as the
overcurrent protection should not be used to protect against overload. The short time
delays associated with short circuit protection do not allow sufficient time for the
orderly curtailment of load by operating personnel. In addition, short circuit protection
set to trip for overload will not allow short-duration, non-damaging overloads – a
practice which is often required in real operating situations.
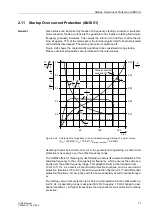
The 7UM62 protective relay features an thermal overload protective function with a
thermal tripping characteristic curve which may be adapted to the overload tolerance
of the equipment being protected.
At the address
you can set the thermal overload protection
OFF
or
ON
, you can block the trip command (
Block relay for trip commands
);
or set the protection function to
Alarm Only
. In that last case no fault record is
created n case of an overload. If the overload protection is switched
ON
, tripping is also
possible.
K–Factor
The overload protection is set in per unit quantities. The nominal current I
N, machine
of
the object to be protected (generator, motor, transformer) is typically used as base
current. The thermally permissible continuous current
I
max prim
can be used to
calculate a factor k
prim
:
The thermally permissible continuous current for the equipment being protected is
indicated in the manufacturer’s specifications. If no specifications are available, a
value of 1.1 times the nominal current rating is assumed.
The
to be set at the 7UM62 (address
) refers to the secondary
nominal current (= device current). The following applies for the conversion:
Example: Generator and current transformer with the following data:
where
I
max prim
Maximum permissible continuous motor current in primary
amperes
I
N Machine
Nominal machine current
I
N CT prim
Current transformer nominal primary current
Permissible continuous current:
I
max prim
= 1.15 ·
I
N, Machine
Generator nominal current
I
N Machine
= 483 A
Current transformer
500 A/1 A
k
prim
I
max prim
I
N, Machine
--------------------------
=
I
max prim
I
N Machine
------------------------
I
N Machine
I
NCT prim
------------------------
⋅
Setting value
=
Setting
x
value K–FACTOR
1 15
,
483 A
500 A
---------------
⋅
1.11
≈
=