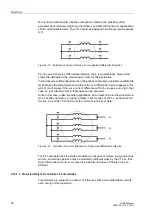
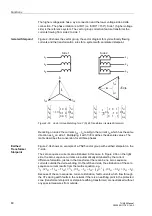
Functions
84
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
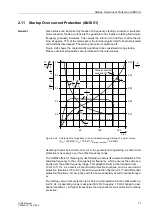
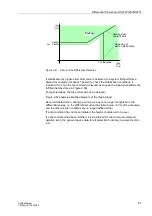
Immediately after the fault (A), the short-circuit currents rise strongly, causing a
equally high stabilizing current (2xthrough-flowing current). Saturation occurring on
one side (B) now causes a differential current and reduces the stabilizing current, so
that the operating point
I
diff
/
I
stab
may move into the tripping area (C).
In contrast, the operating point moves immediately along the fault characteristic (D)
when an internal fault occurs since the stabilization current will barely be higher than
the differential current. Therefore, an internal fault is assumed as soon as the ratio
I
diff
/
I
stab
has exceeded an internal threshold for a fixed minimum time.
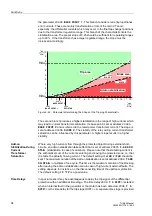
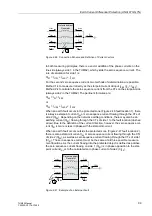
Current transformer saturation in case of an external fault is thus characterized by a
high stabilizing current flowing at the beginning, i.e. by the operating point (diagram
see Figure 2-37) moving into an area that is typical for a high-current external fault
(”add-on stabilization). The add-on stabilization area is limited by the parameter
and the first straight line of the characteristic (with
and
) (see Figure 2-38). The saturation indicator makes its decision within
the first quarter of a period after fault inception. When an external fault is detected, the
differential protection is blocked for a selectable time. The blocking is cancelled as
soon as the operating point
I
diff
/
I
stab
moves steadily (i.e. over 2 periods) within the
tripping area. This allows to detect evolving faults in the protected area reliably even
during an external fault with current transformer saturation.
Figure 2-38
Add-on Stabilization During Current Transformer Saturation
Harmonic
Stabilization
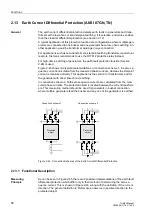
In transformers in particular, high short-time magnetizing currents may be present
during power-up (inrush currents). These currents enter the protected zone but do not
leave it again, so that they act like fault currents entering from one side (Figure 2-39).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12
13
14 15 16 17 18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2031
I DIFF>>
2021
I–DIFF>
2044
BASE POINT 2
BASE POINT 1
2042
Trip area
I
stab
I
NObj
---------------
I
diff
I
NObj
---------------
Block area
2043
SLOPE 2
2041
SLOPE 1
EXF–STAB
2056
Add-on stabilization
b
c
d
a
Fault characteristic