Breaker Failure Protection (ANSI 50BF)
225
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.34
Breaker Failure Protection (ANSI 50BF)
2.34.1 Functional Description
General
The breaker failure protection can be assigned to the current inputs of side 1 or side
2 during the configuration of the protective functions (see Section 2.2). The breaker
failure protection function monitors the reaction of a circuit breaker to a trip signal. In
machine protections, it is typically referred to the mains breaker. To determine if the
circuit breaker has properly opened in response to a trip signal, one of the following
methods is used to ascertain the status of the circuit breaker:
•
Checking whether the current in all three phases drops below a set threshold
following a trip command,
•
Evaluating the position of a circuit breaker auxiliary contact for protective functions,
with which the current criterion is perhaps not expressive, e.g. frequency protection,
voltage protection, rotor earth fault protection.
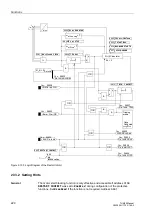
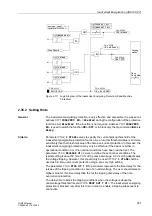
If the circuit breaker has not opened after a programmable time delay (breaker failure),
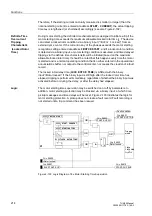
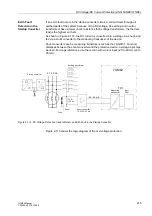
a higher-level circuit breaker can initiate the disconnection (refer to Figure 2-108 as an
example).
Figure 2-108 Functional Principle of the Breaker Failure Protection Function
Initiation
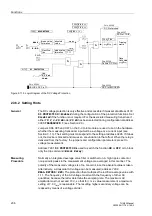
The breaker failure protection function can be initiated by two different sources:
•
Internal protective function of the 7UM62, e.g. trip commands of protective
functions or via CFC (internal logic functions),
•
External trip signals via binary input.
Criteria
The two pickup criteria (current criterion, circuit breaker auxiliary contact) are OR
logics. In case of a tripping without short circuit current, e.g. by the voltage protection
in case of light load, the current is no safe criterion of the circuit breaker response. For
this reason, the pickup is also possible by means of the auxiliary contact criterion.
B/F I>
Protective
&
B/F–Ttrip 0
Breaker Failure Protection
TRIP
B/F”
G
Elements