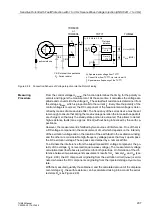
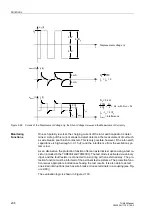
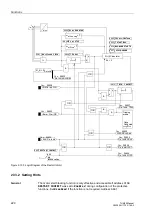
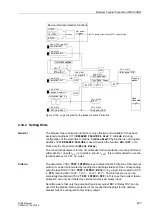
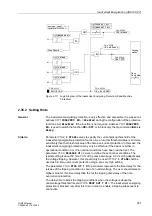
Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
219
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
Extending the
Cooling Time
Constant
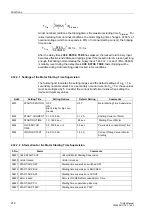
In order to properly account for the reduced heat exchange when a self-ventilated
motor is stopped, the cooling time constants can be increased relative to the time
constants for a running machine by the factor
t at STOP (address
). A stopped
motor is defined by current below an adjustable current flow monitoring threshold
, assuming that the motor idle current is greater than this
threshold. The pickup threshold
affects also the thermal overload
protection function (see Section 2.9).
While the motor is running, the heating of the thermal profile is modeled with the time
constant
τ
L
calculated from the motor ratings, and the cooldown calculated with the
time constant
τ
L
⋅
t at RUNNING (address
). In this way, the protection caters
to the requirements in case of a slow cooldown (slow temperature equilibrium).
Minimum Inhibit
Time
Regardless of thermal profiles, some motor manufacturers require a minimum inhibit
time after the maximum number of permissible starting attempts has been exceeded.
The duration of the inhibit signal depends on which of the times,
or T
ReInhib time
, is longer.
Behaviour in Case
of a Power Supply
Failure
Depending on the setting of parameter
, the value of the thermal
profile is either reset on a failure of the power supply voltage, or cyclically buffered in
a”non-volatile” memory until the power supply voltage returns. In the second case, the
thermal replica uses the last buffered value for calculation and matches it to the
operating conditions.
Emergency
Starting
If, under emergency conditions, motor starting in excess of the maximum allowable
rotor temperature must take place, the motor start blocking signal can be terminated
via a binary input (”
QR”), thus allowing a new starting attempt. The
thermal rotor profile continues to function, however, and the maximum allowable rotor
temperature will be exceeded. No motor shutdown will be initiated by the motor restart
inhibit, but the calculated excessive temperature of the rotor can be observed for risk
assessment.
Blocking
If the motor start blocking function is blocked or switched off, the thermal profile of the
excessive rotor temperature and the equilibrium time
as well as the
minimum inhibit time
are reset, and any existing motor start inhibit
signal is terminated.
Logic
The thermal profile can also be reset via a binary input. This may be useful for testing
and commissioning, and after a power supply voltage failure.
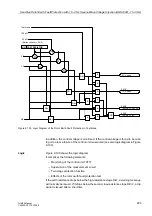
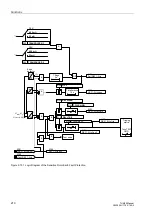
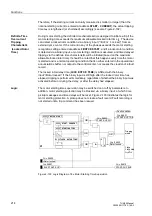
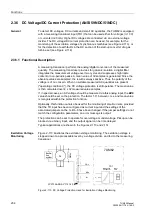
Figure 2-105 shows the logic diagram for the restart inhibit function.