Restart Inhibit for Motors (ANSI 66, 49Rotor)
223
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
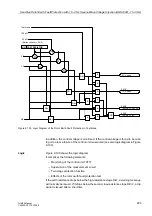
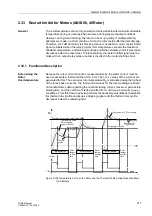
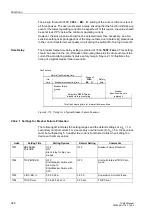
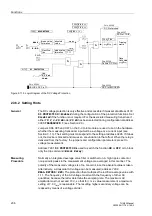
In Figure 2-107, the motor is also restarted twice in warm condition, but the pause
between the restart attempts is longer than in the first example. After the second
restart attempt, the motor is operated at 90 % nominal current. After the shutdown
following the first starting attempt, the thermal profile is “frozen”. After the temperature
equilibrium time (1 min) the rotor cools down with the time constant
τ
L
⋅
≈
5
⋅
204 s = 1020 s. During the second restart, the starting current
causes a temperature rise, whereas the subsequently flowing on-load current of
0.9
⋅
I/I
reduces the temperature. This time, the time constant
τ
L
⋅
t at RUNNING = 2
⋅
204 s = 408 s is effective.
The fact that the restarting limit is exceeded for a short time does not mean a thermal
overload. It rather signals that a thermal overload of the rotor would arise if the motor
were shut down immediately and restarted.
Figure 2-107 Two Warm Restart Followed by Continuous Running
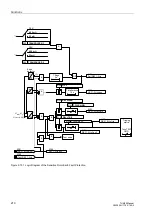
2.33.2.1 Settings of the Restart Inhibit for Motors
0
0.2
200
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
400
800
600
1000
t/s
p.u.
Temperature in p.u.
Motor current in
I
/
I
N
Restarting limit
1st startup
2nd startup
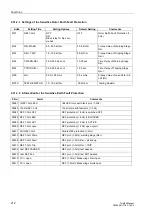
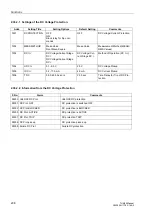
Addr.
Setting Title
Setting Options
Default Setting
Comments
6601
RESTART INHIBIT
OFF
ON
Block relay for trip com-
mands
OFF
Restart Inhibit for Motors
6602
IStart/IMOTnom
1.5..10.0
4.9
I Start / I Motor nominal
6603
T START MAX
3.0..320.0 sec
8.5 sec
Maximum Permissible Starting
Time
6604
T EQUAL
0.0..320.0 min
1.0 min
Temperature Equalization Time
6606
MAX.WARM
STARTS
1..4
2
Permissible Number of Warm
Starts
6607
#COLD-#WARM
1..2
1
Number of Cold Starts - Warm
Starts