Functions
48
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.8
Inverse-Time Overcurrent Protection (ANSI 51V)
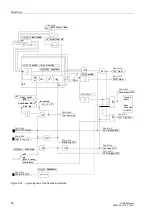
2.8.1
Functional Description
General
The overcurrent time protection represents the short-circuit protection for small or low-
voltage machines. For larger machines it is used as back-up protection for the
machine short-circuit protection (differential protection and/or impedance protection).
It provides back-up protection for network faults which are not promptly disconnected
and thus may endanger the machine.
The 7UM62 relay allows to choose between the input transformers of side 1 and side
2 for allocation of the inverse-time overcurrent protection function. This choice is made
during configuration (see Section 2.2).
In generators where the excitation voltage is derived from the machine terminals, the
short-circuit current subsides quickly in the event of close-up faults (i.e. in the
generator or unit transformer range) due to the absence of excitation voltage the
current decreases within a few seconds to a value below the pick-up value of the
overcurrent time protection. In order to avoid a drop out of the pickup, the positive-
sequence component is monitored additionally. This component can influence the
overcurrent detection according to two different methods. The influence of the
undervoltage can be switched off.
The protective function operates, depending on the ordering variant, with an inverse
current-tripping characteristic according to the IEC or ANSI standards. The
characteristic curves and the corresponding formulas are represented in Technical
Data (Figures 4-1 to 4-3 in Section 4.3). If one of the inverse characteristics (IEC or
ANSI) are configured, the definite-time stages I>> and I> can be additionally effective
(see Section 2.6 and 2.7).
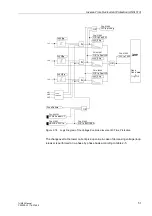
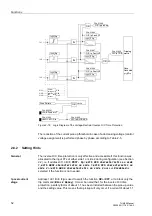
Pickup /
Trip
Each phase current is compared individually with the common
setting value. If a
current exceeds 1.1 times the set value, the stage picks up and is signalled on a per
phase basis. The r.m.s. values of the fundamental component are used for the pickup.
During the pickup of an Ip stage, the tripping time is calculated from the flowing fault
current by means of an integrated measuring procedure, depending on the selected
tripping characteristic. A trip command is transmitted after this time expires.
Dropout
The dropout of a picked up stage is performed as soon as the value falls below
approximately 95 % of the pickup value (i.e. 0.95
⋅
1.1 = 1.045
⋅
setting value). The
timer will start again for all new pickups.
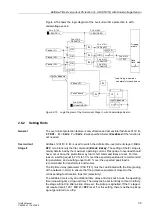
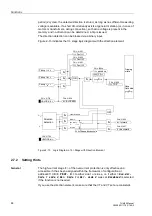
Undervoltage
Consideration
The inverse O/C time protection is equipped with a undervoltage detection that can be
disabled. This function can influence the overcurrent detection in two different ways:
•
Voltage controlled:
If the value falls below a settable voltage threshold, an overcurrent stage with a
lower pick-up value is enabled.
•
Voltage restraint:
The pickup threshold of the overcurrent stage depends on the voltage level. A lower
voltage reduces the current pick-up value (see Figure 2-16). A linear, directly
proportional dependency is realized in the zone between U/U
Nom
= 1.00 and 0.25.
Consequently, the following rule applies: