Display System Structure
You use the display system to manage display properties and view assignments for objects in your project. You can also
create new groupings for display purposes.
Elements of the Display System
The display system has 3 major elements:
■
A display representation, which controls how an individual object, such as a door or a wall, is displayed
■
A display set, which is a group of display representations of objects
■
A display configuration, which is a collection of display sets assigned to particular view directions
These 3 elements are hierarchical: each display configuration contains a number of display sets, and each display set
contains a number of display representations. To use a display configuration, you assign it to a viewport. The objects
in the viewport then use the display properties specified in the display configuration.
Predefined Display Configurations in Templates
You use different display configurations for different tasks, such as sketching and plotting. You also use different display
configurations for different types of drawings, such as floor plans, 3D models, and elevations.
AutoCAD Architecture includes templates with predefined display configurations applied to viewports. These
configurations are created for typical architectural tasks and drawing types. You can use the configurations and viewports
supplied by the templates, or you can modify the display system settings to suit your office standards. If you want to
create your own display configurations, you can start a drawing from scratch or from a template that does not contain
predefined display configurations.
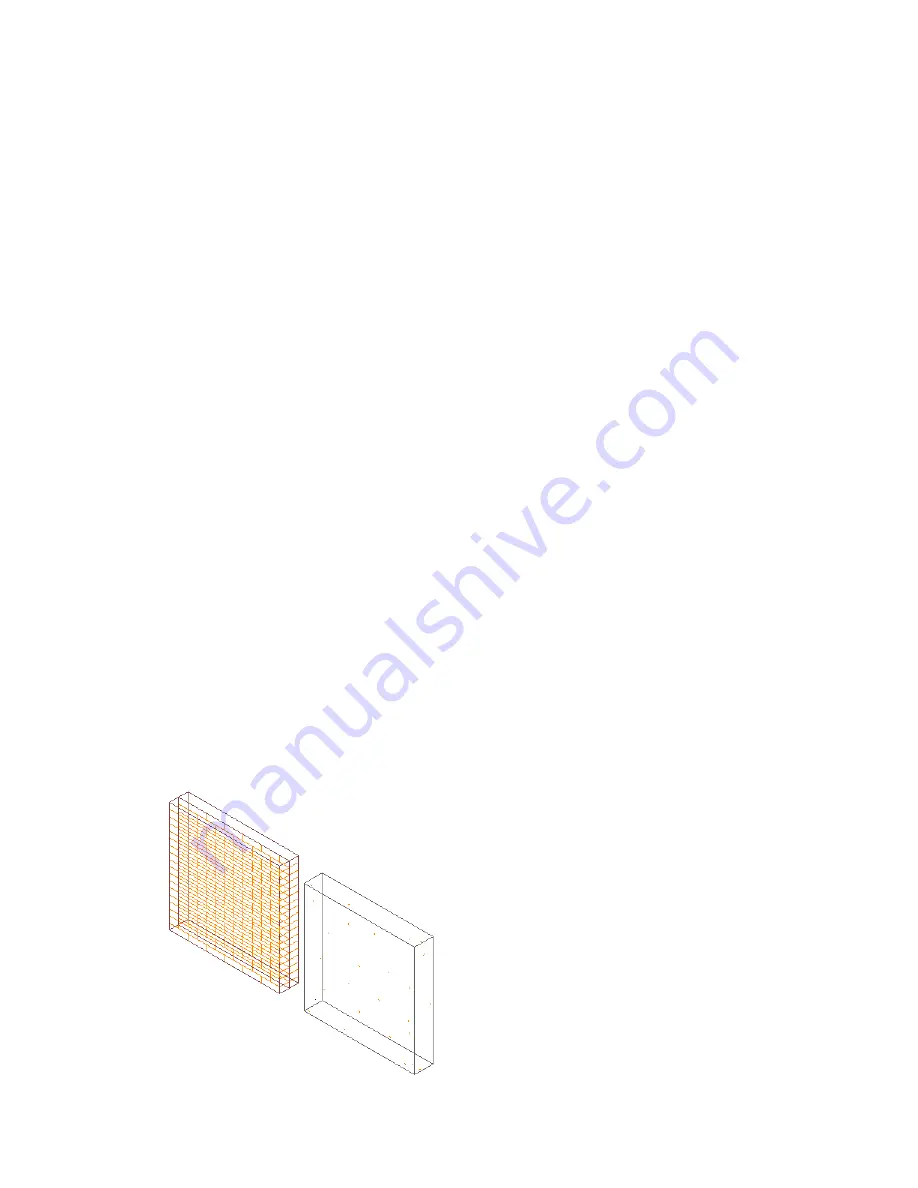
Materials and the Display System
A material definition is a group of settings for the display properties of a real-world material, such as glass, brick, or
wood. The settings define how the components assigned to the material appear in every view.
The materials feature works with the display system to simplify the process of customizing the display of drawings.
Rather than specifying individual properties, you can control the display of objects according to the materials assigned
to the physical components of the objects.
For example, you can assign brick as the material for all walls whose components consist of this material. The display
properties of the bricks are customized to look like a typical brick wall. By assigning the material to walls, you avoid
the need to customize the display properties for each wall that uses brick material. In addition, if the materials change
during the project, you can reassign components to the new material.
Wall components assigned brick and concrete materials
450 | Chapter 10 Display System
Summary of Contents for 00128-051462-9310 - AUTOCAD 2008 COMM UPG FRM 2005 DVD
Page 1: ...AutoCAD Architecture 2008 User s Guide 2007 ...
Page 4: ...1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
Page 40: ...xl Contents ...
Page 41: ...Workflow and User Interface 1 1 ...
Page 42: ...2 Chapter 1 Workflow and User Interface ...
Page 146: ...106 Chapter 3 Content Browser ...
Page 164: ...124 Chapter 4 Creating and Saving Drawings ...
Page 370: ...330 Chapter 6 Drawing Management ...
Page 440: ...400 Chapter 8 Drawing Compare ...
Page 528: ...488 Chapter 10 Display System ...
Page 540: ...500 Chapter 11 Style Manager ...
Page 612: ...572 Chapter 13 Content Creation Guidelines ...
Page 613: ...Conceptual Design 2 573 ...
Page 614: ...574 Chapter 14 Conceptual Design ...
Page 678: ...638 Chapter 16 ObjectViewer ...
Page 683: ...Designing with Architectural Objects 3 643 ...
Page 684: ...644 Chapter 18 Designing with Architectural Objects ...
Page 788: ...748 Chapter 18 Walls ...
Page 942: ...902 Chapter 19 Curtain Walls ...
Page 1042: ...1002 Chapter 21 AEC Polygons ...
Page 1052: ...Changing a door width 1012 Chapter 22 Doors ...
Page 1106: ...Changing a window width 1066 Chapter 23 Windows ...
Page 1172: ...1132 Chapter 24 Openings ...
Page 1226: ...Using grips to change the flight width of a spiral stair run 1186 Chapter 25 Stairs ...
Page 1368: ...Using the Angle grip to edit slab slope 1328 Chapter 28 Slabs and Roof Slabs ...
Page 1491: ...Design Utilities 4 1451 ...
Page 1492: ...1452 Chapter 30 Design Utilities ...
Page 1536: ...1496 Chapter 31 Layout Curves and Grids ...
Page 1564: ...1524 Chapter 32 Grids ...
Page 1611: ...Documentation 5 1571 ...
Page 1612: ...1572 Chapter 36 Documentation ...
Page 1706: ...Stretching a surface opening Moving a surface opening 1666 Chapter 36 Spaces ...
Page 1710: ...Offsetting the edge of a window opening on a freeform space surface 1670 Chapter 36 Spaces ...
Page 1956: ...1916 Chapter 42 Fields ...
Page 2035: ...Properties of a detail callout The Properties of a Callout Tool 1995 ...
Page 2060: ...2020 Chapter 45 Callouts ...
Page 2170: ...2130 Chapter 47 AEC Content and DesignCenter ...
Page 2171: ...Other Utilities 6 2131 ...
Page 2172: ...2132 Chapter 48 Other Utilities ...
Page 2182: ...2142 Chapter 51 Reference AEC Objects ...
Page 2212: ...2172 Chapter 52 Customizing and Adding New Content for Detail Components ...
Page 2217: ...AutoCAD Architecture 2008 Menus 54 2177 ...
Page 2226: ...2186 Chapter 54 AutoCAD Architecture 2008 Menus ...
Page 2268: ...2228 Index ...