Doors
A door is an AEC object that interacts with walls and door and window assemblies. You can also create freestanding
doors for door-type drawings.
Creating Doors
You can create doors using the typical design parameters for style, standard size, width and height, threshold height,
and head height. You can choose styles with glass shapes that receive standard muntins patterns, and create your own
custom glass shapes from profiles.
Door Styles
AutoCAD Architecture provides ready-to-use door styles. The design rules of a door style determine the default dimensions
of doors and the door shape and type
■
The door shape determines the geometry of the door panel, such as rectangular, half-round, and arch. You can
also create custom door shapes from profiles.
■
The door type determines the number of panels and the method of opening the door, such as single, double, bifold,
pocket, revolving, and overhead.
You can define standard sizes in a door style and then select the size you want to use when you place the door in a
drawing.
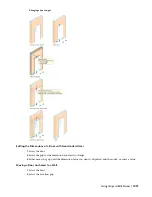
Anchoring Doors
After a door is placed in a wall or door and window assembly, the door is constrained to the object and cannot move
outside it.
Doors can also be anchored to specific locations in walls or door and window assemblies, so that when the wall or door
and window assembly moves or changes size, the location of the door in that object remains constant.
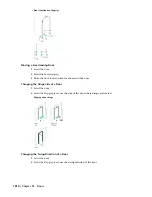
Door Dimensions
Some door dimensions depend on the shape and type specified in the door style.
Rise is the height from the top of the rectangular portion of a door to the peak of the door opening for Gothic, Arch,
and Peak Pentagon door shapes.
Leaf specifies the door size for pairs of Uneven, Uneven-Dhung, and Uneven Opposing door types. For more information
about leaf, see “
Changing the Door Leaf
” on page 1016.
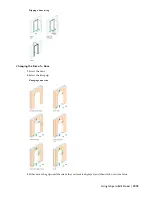
Vertical Alignment of Doors
You use vertical alignment settings to control the placement of the door in the wall, the location of the working point
vertically in the wall, and how the door responds to modifications in height. To determine the working point on the
door, use the threshold and head height settings. You can place the working point at the sill or at the head. For example,
if you specify the vertical alignment as 0'' and the door height as 7'–0'', the door opening height is 7’–0''. If you next
specify the height of the door as 6'–8'', the door threshold remains at 0'' and the door opening height becomes 6’–8''.
For the door head working point, if you specify the vertical alignment as 7'–0'' and the door height as 7'–0'', the door
opening height is 7–0''. If you specify the door height as 6'–8'', the door head remains at 7'–0'' and the door threshold
becomes 4''.
Materials in Doors
You can assign materials to a door. Materials are displayed in wireframe and working shade views, or when rendered.
Materials have specific settings for individual components of a door, such as the panel, the stop, the frame, or a glass
inset.
1004 | Chapter 22 Doors
Summary of Contents for 00128-051462-9310 - AUTOCAD 2008 COMM UPG FRM 2005 DVD
Page 1: ...AutoCAD Architecture 2008 User s Guide 2007 ...
Page 4: ...1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
Page 40: ...xl Contents ...
Page 41: ...Workflow and User Interface 1 1 ...
Page 42: ...2 Chapter 1 Workflow and User Interface ...
Page 146: ...106 Chapter 3 Content Browser ...
Page 164: ...124 Chapter 4 Creating and Saving Drawings ...
Page 370: ...330 Chapter 6 Drawing Management ...
Page 440: ...400 Chapter 8 Drawing Compare ...
Page 528: ...488 Chapter 10 Display System ...
Page 540: ...500 Chapter 11 Style Manager ...
Page 612: ...572 Chapter 13 Content Creation Guidelines ...
Page 613: ...Conceptual Design 2 573 ...
Page 614: ...574 Chapter 14 Conceptual Design ...
Page 678: ...638 Chapter 16 ObjectViewer ...
Page 683: ...Designing with Architectural Objects 3 643 ...
Page 684: ...644 Chapter 18 Designing with Architectural Objects ...
Page 788: ...748 Chapter 18 Walls ...
Page 942: ...902 Chapter 19 Curtain Walls ...
Page 1042: ...1002 Chapter 21 AEC Polygons ...
Page 1052: ...Changing a door width 1012 Chapter 22 Doors ...
Page 1106: ...Changing a window width 1066 Chapter 23 Windows ...
Page 1172: ...1132 Chapter 24 Openings ...
Page 1226: ...Using grips to change the flight width of a spiral stair run 1186 Chapter 25 Stairs ...
Page 1368: ...Using the Angle grip to edit slab slope 1328 Chapter 28 Slabs and Roof Slabs ...
Page 1491: ...Design Utilities 4 1451 ...
Page 1492: ...1452 Chapter 30 Design Utilities ...
Page 1536: ...1496 Chapter 31 Layout Curves and Grids ...
Page 1564: ...1524 Chapter 32 Grids ...
Page 1611: ...Documentation 5 1571 ...
Page 1612: ...1572 Chapter 36 Documentation ...
Page 1706: ...Stretching a surface opening Moving a surface opening 1666 Chapter 36 Spaces ...
Page 1710: ...Offsetting the edge of a window opening on a freeform space surface 1670 Chapter 36 Spaces ...
Page 1956: ...1916 Chapter 42 Fields ...
Page 2035: ...Properties of a detail callout The Properties of a Callout Tool 1995 ...
Page 2060: ...2020 Chapter 45 Callouts ...
Page 2170: ...2130 Chapter 47 AEC Content and DesignCenter ...
Page 2171: ...Other Utilities 6 2131 ...
Page 2172: ...2132 Chapter 48 Other Utilities ...
Page 2182: ...2142 Chapter 51 Reference AEC Objects ...
Page 2212: ...2172 Chapter 52 Customizing and Adding New Content for Detail Components ...
Page 2217: ...AutoCAD Architecture 2008 Menus 54 2177 ...
Page 2226: ...2186 Chapter 54 AutoCAD Architecture 2008 Menus ...
Page 2268: ...2228 Index ...