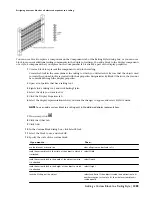
Roofs
Roofs are AEC objects that you can use to model an entire multiple-face roof surface. You can create roofs independently
of other objects, or you can place a roof on a shape defined by a polyline or by a closed set of walls. After creating the
roof, you can change its overall dimensions and slope, or edit its edges and faces individually. For more flexibility in
customizing a roof, you can convert it to a collection of individual roof slabs.
Roof Slabs
A roof slab models a single face of a roof. Roof slab objects also differ from roof objects in that each roof slab is a separate
entity with no direct connection to other entities. When you use multiple roof slabs to model an entire roof surface,
you have more flexibility in editing the roof, but the combined topology (3D geometry) of the roof is not calculated
automatically. For this reason, it is recommended that when you design complex roofs, you start with a roof object.
Then, when the design is substantially complete, but you need more flexibility for customizing edges and other details,
you can convert the roof to individual roof slabs. For information on creating and editing roof slabs, see “
Slabs and
Roof Slabs
” on page 1303.
While roof slabs do not dynamically interact with each other, they do allow significant control over the roof geometry.
For example, you can trim roof slabs individually, extend them, and miter them with other roof slabs. You can also
cut holes in roof slabs, add or subtract mass elements, and apply detailed fascia and soffit profiles to any edge at any
angle and orientation. Because roof slabs are style-based, you can apply design changes globally.
Materials in Roofs
You can assign materials to a roof. Materials are displayed in wireframe and working shade views, or when rendered.
Materials have specific settings for the physical components of a roof, such as slab. For more information see “
Material
Components and Display Properties
” on page 510.
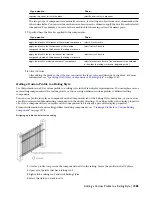
Viewing roofs in 2D wireframe and rendered views
AutoCAD Architecture provides predefined materials for common design purposes. These materials contain settings
for roof components. You can use the predefined materials as they are, or modify them for your designs. You can also
create your own materials. Object styles provided with the software have appropriate materials already assigned to
them. For more information, see “
Slab/Roof Slab Materials and Display Components
” on page 1355and “
Material
Components and Display Properties
” on page 510.
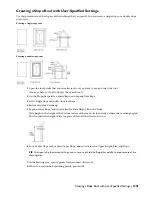
Using Roof Tools to Create Roofs
Tools provided with AutoCAD Architecture let you quickly place roofs by selecting a roof tool with a specific roof style
and other predefined properties. You can use the tool with all of its default settings, or you can change any properties
that are not controlled by the style. You can create roofs with single or double slopes and gable roofs. You can also use
roof tools to create new roofs by applying tool properties to existing polylines and walls.
1290 | Chapter 27 Roofs
Summary of Contents for 00128-051462-9310 - AUTOCAD 2008 COMM UPG FRM 2005 DVD
Page 1: ...AutoCAD Architecture 2008 User s Guide 2007 ...
Page 4: ...1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
Page 40: ...xl Contents ...
Page 41: ...Workflow and User Interface 1 1 ...
Page 42: ...2 Chapter 1 Workflow and User Interface ...
Page 146: ...106 Chapter 3 Content Browser ...
Page 164: ...124 Chapter 4 Creating and Saving Drawings ...
Page 370: ...330 Chapter 6 Drawing Management ...
Page 440: ...400 Chapter 8 Drawing Compare ...
Page 528: ...488 Chapter 10 Display System ...
Page 540: ...500 Chapter 11 Style Manager ...
Page 612: ...572 Chapter 13 Content Creation Guidelines ...
Page 613: ...Conceptual Design 2 573 ...
Page 614: ...574 Chapter 14 Conceptual Design ...
Page 678: ...638 Chapter 16 ObjectViewer ...
Page 683: ...Designing with Architectural Objects 3 643 ...
Page 684: ...644 Chapter 18 Designing with Architectural Objects ...
Page 788: ...748 Chapter 18 Walls ...
Page 942: ...902 Chapter 19 Curtain Walls ...
Page 1042: ...1002 Chapter 21 AEC Polygons ...
Page 1052: ...Changing a door width 1012 Chapter 22 Doors ...
Page 1106: ...Changing a window width 1066 Chapter 23 Windows ...
Page 1172: ...1132 Chapter 24 Openings ...
Page 1226: ...Using grips to change the flight width of a spiral stair run 1186 Chapter 25 Stairs ...
Page 1368: ...Using the Angle grip to edit slab slope 1328 Chapter 28 Slabs and Roof Slabs ...
Page 1491: ...Design Utilities 4 1451 ...
Page 1492: ...1452 Chapter 30 Design Utilities ...
Page 1536: ...1496 Chapter 31 Layout Curves and Grids ...
Page 1564: ...1524 Chapter 32 Grids ...
Page 1611: ...Documentation 5 1571 ...
Page 1612: ...1572 Chapter 36 Documentation ...
Page 1706: ...Stretching a surface opening Moving a surface opening 1666 Chapter 36 Spaces ...
Page 1710: ...Offsetting the edge of a window opening on a freeform space surface 1670 Chapter 36 Spaces ...
Page 1956: ...1916 Chapter 42 Fields ...
Page 2035: ...Properties of a detail callout The Properties of a Callout Tool 1995 ...
Page 2060: ...2020 Chapter 45 Callouts ...
Page 2170: ...2130 Chapter 47 AEC Content and DesignCenter ...
Page 2171: ...Other Utilities 6 2131 ...
Page 2172: ...2132 Chapter 48 Other Utilities ...
Page 2182: ...2142 Chapter 51 Reference AEC Objects ...
Page 2212: ...2172 Chapter 52 Customizing and Adding New Content for Detail Components ...
Page 2217: ...AutoCAD Architecture 2008 Menus 54 2177 ...
Page 2226: ...2186 Chapter 54 AutoCAD Architecture 2008 Menus ...
Page 2268: ...2228 Index ...