Appendix - 42
MELSEC-A
APPENDICES
PARAMETER
This is the basic data used in positioning.
Parameters are determined by the machine
side design, so subsequent changes of
parameters must be accompanied by changes
in the machine design.
Data cannot be written during positioning. The
initial parameter values are written by the
maker.
POSITION CONTROL
This is mainly the control of position and
dimension, such as in fixed-dimension feed,
positioning, numerical control, etc. This is
always controlled with feed pulses. There is
also speed control.
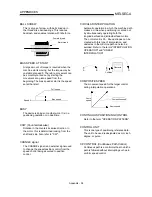
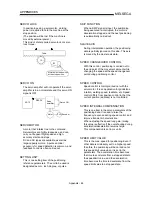
POSITION LOOP GAIN
This is the ratio of the deviation counter droop
pulse count to the command speed (pulse/s).
Command speed
Position
loop gain
=
Droop pulse count
(1/s)
The position loop gain can be set with the
servo amplifier. Raise the gain to improve the
stopping accuracy. However, overshooting will
occur if the position loop gain is raised too far,
and the operation will become unstable.
If the position loop gain is lowered too far, the
machine will stop more smoothly but the
stopping error will increase.
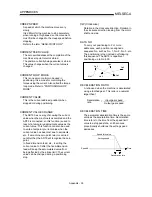
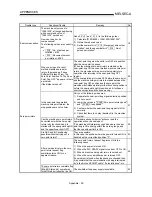
POSITION LOOP MODE
This is one servo control mode used in
positioning. It is a mode for carrying out
position control. The other servo control
modes are the speed loop mode for carrying
out speed control, and the torque loop mode
for carrying out torque control (current control).
M
PLG
Servo amplifier
Servomotor
Pulse train
Droop pulses
Posi-
tion
control
Speed
control
Cur-
rent
control
Inverter
Current feedback
Speed feedback
Position feedback
Interface
POSITIONING
Accurately moving the machine from a point to
a determined point. The distance, direction,
speed, etc., for that movement are designated
by the user. Positioning is used in operations
such as cutting sheets, drilling holes in plates,
mounting parts on a PCB, and welding.
Positioning is also used with robots.
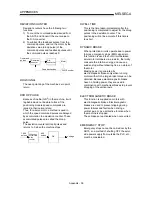
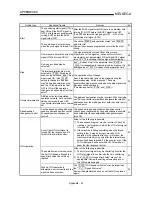
POSITIONING COMPLETE SIGNAL
This is a signal that occurs when the
positioning is complete. A timer set beforehand
starts when this signal is output, and the
machine movement stops for that time.
This signal is used to turn OFF the positioning
start signal.
Dwell time
Positioning complete
signal
Positioning
Different type of work
Time
POSITIONING DATA
This is data for the user to carry out
positioning. The No. of points to which
positioning is carried out (the No. of
addresses) is designated by the user. In the
AD75, this is a maximum of 600 points.
As a principle, positioning is executed in the
order of the data Nos.
POSITIONING PARAMETER
This is basic data for carrying out positioning
control. Types of data include control unit,
movement amount per pulse, speed limit
value, upper and lower stroke limit values,
acceleration/deceleration time, positioning
method, etc.
Parameters have an initial value, so that value
is changed to match the control conditions.
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......