Appendix - 33
MELSEC-A
APPENDICES
ADDRESS
1) This is a numerical value to express the
positioning position, designated in mm, inch,
angle, or No. of pulse units.
2) The memory address. Many addresses are
stored in the memory. An address is read or
written after it is designated.
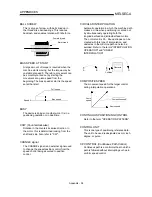
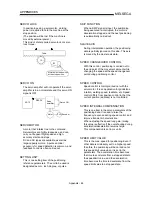
AFTER mode
This is the mode that outputs the M code after
positioning is complete (after stopping).
Clamping can be commanded, drilling
dimensions can be selected, etc., with this
mode.
OFF
ON
No.11
No.10
Positioning
M code (8)
Clamp command
AUTO TUNING (Automatic Tuning)
Properties such as responsiveness and
stability of machines driven with a servomotor
are affected by changes in the inertia moment
and rigidity due to changes in the machine
load, etc.
This function automatically adjusts the speed
loop gain and position loop gain to match the
machine state, so the machine's performance
can be maintained at its optimum state.
A real time automatic tuning function should be
used for machines having large load
fluctuations.
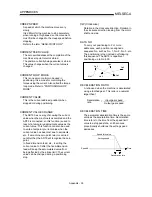
AUTOMATIC TRAPEZOIDAL
ACCELERATION/DECELERATION
An operation in which a graph of the time and
speed takes a trapezoidal shape.
Acceleration
Speed
Time
Deceleration
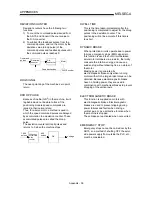
BACKLASH COMPENSATION
When a forward run operation changes to a
reverse run operation, there is sometimes play
(backlash) in the mesh of the toothed gears.
This also occurs when using a worm gear.
Because of this backlash, a left feed of 1m
carried out after a right feed of 1m will not be
sufficient to return the machine to its original
position. The machine cannot be positioned to
its original position without an extra feed
equivalent to the backlash amount. This
function compensates for that backlash
amount.
Backlash
Forward run
1m (right feed)
Machine
does not
move.
Backlash
1m (left feed)
(Left feed amount)
BACKUP FUNCTION
Backup functions consist of the following.
1) Functions for storing the sequence program
and device statuses stored in the RAM
memory of the PLC CPU, so that they are
not lost during power failures, etc.
2) Functions for storing the current value in
absolute position compatible systems so
that it is not lost during power failures, etc.
3) Functions for reading the PLC CPU data
(PLC programs, parameters, positioning
data, etc.) by a peripheral device when the
old CPU is replaced, and then write it to the
new PLC CPU after the replacement is
completed.
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......