12 - 63
MELSEC-A
12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS
Example 2.
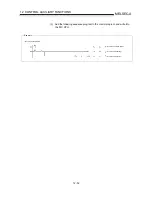
(1) Using Expression 1, calculate the positioning address that can be specified in
the system where the zero point address in Example 1 is 214740000.0 (µm).
•
Lower limit value of positioning address
(Positioning address) = 0.1 (-268435456) + 214740000.0
= 187896454.4 (µm)
•
Upper limit value of positioning address
(Positioning address) = 0.1 268 214740000.0
= 241583545.5 (µm)
(2) Since the lower limit value of the calculated positioning address is within the
range of Condition 2, the calculated address 187896454.4 (µm) is the lower
limit for positioning in the absolute position detection system.
Since the upper limit value of the calculated positioning address is outside the
range of Condition 2, the upper limit value 214748364.7 (µm) in the positioning
range of Condition 2 is the upper limit for positioning in the absolute position
detection system.
Use the AD75 within the range 187896454.4 (µm) to 214748364.7 (µm) in the
absolute position detection system.
For positioning in excess of 187896454.4 (µm), the AD75 cannot be used in
the absolute position detection system.
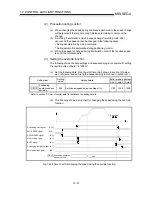
Positioning address specifying range
Setting cannot
be made
241583545.5
214740000.0
187896454.4
Unusable range in absolute
position detection system
214748364.7
-214748364.8
Usable range in absolute
position detection system
Unit:
µ
m
(Zero point)
Example 3.
(1) The conditions for calculating the positioning address are indicated below.
•
Movement amount per pulse: 0.9 (µm)
•
Zero point address: 0.0 (µm)
•
Number of feedback pulses = 8192 (pulse)
(2) Calculate the positioning address from the range of using the number of output
pulses in Condition 1 and the expression for calculating the positioning
address (Expression 1).
•
Lower limit value of positioning address (use the number of negative side
pulses in Condition 1 for calculation)
(Positioning address) = (movement amount per pulse) (number of output
pulses) + (zero point address)
= 0.9 (-268435456) + 0.0
= -241591910.4 (µm)
•
Upper limit value of positioning address (use the number of positive side
pulses in Condition 1 for calculation)
(Positioning address) = (movement amount per pulse) (number of output
pulses) + (zero point address)
= 0.9 268 0.0
= 241591909.5 (µm)
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......