8 - 4
MELSEC-A
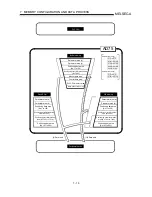
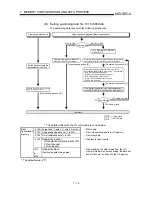
8 ZERO POINT RETURN CONTROL
8.2 Machine zero point return
8.2.1 Outline of the machine zero point return operation
Important
Use the zero point return retry function when the zero point position is not always in
the same direction from the workpiece operation area (when the zero point is not
set near the upper or lower limit of the machine).
* The machine zero point return may not complete unless the zero point return retry
function is used.
Machine zero point return operation
In a machine zero point return, establish a machine zero point.
In the zero point return methods (1) to (5), the address information stored in the
AD75, PLC CPU and servo amplifier is never used.
In the zero point return method (6): data setting method, the address information of
the servo held by the absolute position detection system is used.
The position mechanically established after the machine zero point return is
regarded as the "zero point" to be the starting point for positioning control.
The method for establishing a "zero point" by a machine zero point return differs
according to the method set in " Pr.45 Zero point return method".
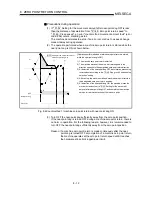
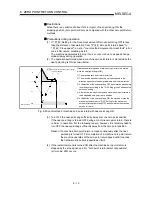
The following shows the operation when starting a machine zero point return.
1) The machine zero point return is started.
2)
The operation starts according to the speed and direction set in the zero point return
parameters (
Pr.45
to
Pr.59
).
3)
The "zero point" is established by the method set in "
Pr.45
Zero point return method",
and the machine stops. (Refer to sections 8.2.2 to 8.2.8)
4)
If "a" is set in "
Pr.47
Zero point address", "a" will be stored as the current position in the
"
Md.29
Current feed value" and "
Md.30
Machine feed value" which are monitoring the
position.
5) "
Pr.47
Zero point address" ("a") is stored in the "
Md.43
Zero point absolute position".
6) The machine zero point return is completed.
* The " Pr.47 Zero point address" is a fixed value set by the user, but the
" Md.43 Zero point absolute position" is constantly changed by the AD75 to
indicate the "zero point", even if there is a change in the address information.
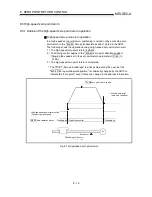
M
Zero point
Near-point dog
Machine zero point return
Fig. 8.1 Example of a machine zero point return
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......