1 - 9
MELSEC-A
1 PRODUCT OUTLINE
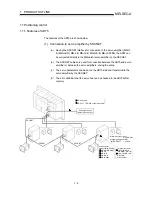
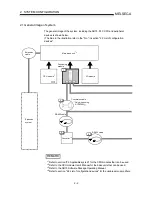
The principle of "position control" and "speed control" operation is shown below.
Position control
The total number of pulses in a pulse train required to move the designated distance
is obtained in the following manner.
Movement amount of machine (load)
side when motor rotates once
Designated distance
No. of pulses required
for servomotor to rotate
once
Total number of
pulses in a pulse
train required to
move designated
distance
* The No. of pulses required for the servomotor to rotate once is the "pulse encoder
resolution" described in the servomotor catalog specification list.
When this total number of pulses in a pulse train is issued from the AD75 to the servo
amplifier, control to move the designated distance can be executed.
The machine side movement amount when one pulse is issued to the servo amplifier is
called the "movement amount per pulse". This value is the min. value for the workpiece
to move, and is also the electrical positioning precision.
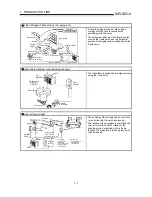
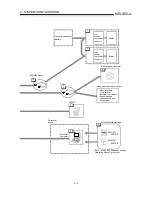
Speed control
The above "total number of pulses in a pulse train" is an element required for
movement distance control, but when carrying out positioning control or speed
control, the speed must also be controlled.
This "speed" is controlled by the "pulse train frequency".
Positioning
module
Servo
amplifier
Servomotor
Detector
Speed = Pulse frequency
Movement amount = No. of pulses
Feedback pulses =
Pulses generated by detector
Feedback pulse
(Pulse
encoder)
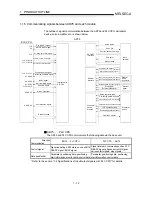
A
ta
td
0.4
1.2
0.4
(s)
Pulse frequency
[pps]
This area is the total
No. of commanded
pulse train.
Movement amount t = 2
Fig.1.1 Relationship between position control and speed control
POINT
The AD75 controls the position with the "total number of pulses in a pulse train",
and the speed with the "pulse train frequency".
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......