Appendix - 41
MELSEC-A
APPENDICES
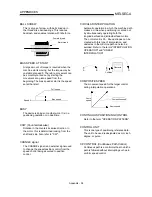
MASTER AXIS
When carrying out interpolation operations,
this is the side on which the positioning data is
executed in priority. For example, when
positioning with the X axis and Y axis, the side
with the largest movement distance will
become the master axis, and the speed will
follow that axis. The slave axis speed will be
ignored.
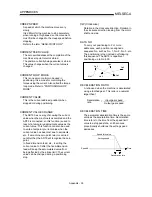
MOVEMENT AMOUNT PER PULSE
When using mm, inch, or angle units, the
movement amount is calculated and output
from the machine side showing how much the
motor shaft moves per pulse. Positioning
accuracy in smaller units is not possible.
On the motor side, the movement amount per
axis rotation is normally designed as a
reference, so it is calculated as follows.
Movement amount per pulse =
P rate
No. of pulses per
encoder rotation
×
Movement amount
per rotation
Amount the motor moves (travel) per pulse.
MULTIPLYING RATE SETTING
The P rate. Refer to the term "P RATE".
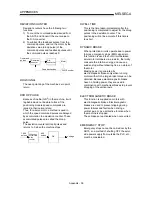
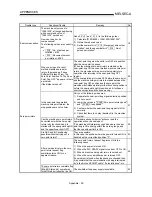
NEAR-POINT DOG
This is a switch placed before the zero point.
When this switch turns ON, the feedrate is
changed to the creep speed. Because of that,
the time that this switch is ON must be long
enough to allow for the time required for
deceleration from the feedrate to the creep
speed.
ON
OFF
Feedrate
Creep speed
Time
Near-point dog
OPERATION PATTERN
The kind of operation to be carried out after
executing the positioning data is determined.
1) If "POSITIONING COMPLETE" is selected,
the operation will stop after the positioning
is complete.
2) If "CONTINUOUS POSITIONING
CONTROL" is selected, the next data No.
will be automatically executed after the
positioning is complete.
3) If "CONTINUOUS PATH CONTROL" is
selected, the positioning will not be
completed. Only the speed will be
automatically changed, and the next data
No. will be executed.
OVERRIDE FUNCTION
With this function, the speed during positioning
operations (current speed) can be varied
between 1 and 300%.
The speed can also be changed by the same
variable rate for continuous positioning with
differing designated speeds.
P RATE (Pulse Rate)
A coefficient that magnifies the feedback
pulses per motor shaft rotation by 2-fold, 3-
fold, 1/2 or 1/3.
It is the ratio of the feed pulses and feedback
pulses.
For example, when the No. of pulses per
motor shaft rotation is set to 2400 pulses, and
the P rate is set to 2, the result will be
equivalent to 1200 pulses.
The rotation per pulse is 0.15° when 2400
pulses per rotation are set, but this becomes
0.3° when 1200 pulses. The positioning
accuracy drops as the P rate is increased.
PANCAKE MOTOR
The axial dimension of this motor is approx.
100mm shorter than that of a standard motor.
This type of motor is used when the
servomotor installation space is narrow.
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......