Appendix - 35
MELSEC-A
APPENDICES
CREEP SPEED
A speed at which the machine moves very
slowly.
It is difficult for the machine to stop accurately
when running at high speed, so the movement
must first be changed to the creep speed before
stopping.
Refer to the term "NEAR-POINT DOG".
CURRENT FEED VALUE
The zero point address at the completion of the
machine zero point return is stored.
The position currently being executed is stored.
This value changes when the current value is
changed.
CURRENT LOOP MODE
This is one servo control mode used in
positioning. It is a mode for controlling the
torque using the current. Also called the torque
loop mode. Refer to "POSITIONING LOOP
MODE".
CURRENT VALUE
This is the current address (position) when
stopped or during positioning.
CURRENT VALUE CHANGE
The AD75 has no way of knowing the current
value when the machine is assembled and the
AD75 is connected, so this function is used to
teach it a temporary approximate value as the
current value. This function can also be used
to write a temporary current value when the
current value has been lost due to accidents,
etc. If a machine zero point return is carried
out after that, the AD75 will recognize the zero
point.
In fixed-dimension feed, etc., rewriting the
current value to 0 after the fixed-dimension
feed will keep the accumulated value from
being affected by the stroke limit. The current
value can be changed during a positioning
stop.
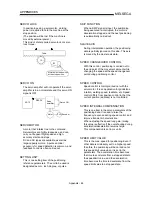
CW (Clockwise)
Rotation in the clockwise direction. Rotation in
the clockwise direction looking from the motor
shaft end side.
DATA NO.
To carry out positioning to 2 or more
addresses, each position is assigned a
sequence No. such as No. 1, No. 2, No. 3, etc.
The positioning is then carried out following
this sequence. The AD75 is capable of
positioning up to No. 600.
No.1
No.2
No.3
No.4
No.5
No.6
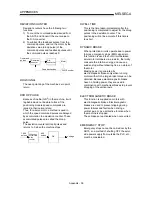
DECELERATION RATIO
A ratio used when the machine is decelerated
using a toothed gear. This ratio is a numeral
larger than 1.
Input gear speed
Deceleration
ratio
=
Output gear speed
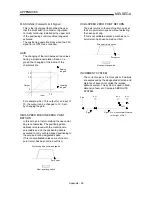
DECELERATION TIME
The parameter deceleration time is the same
value as the acceleration time. Deceleration
time refers to the time from the speed limit
value to a stopped state, so it becomes
proportionally shorter as the setting speed
decreases.
Speed limit value
Setting speed
Speed 0
Deceleration time
Time
Summary of Contents for A1SD75M1
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...A 18 MEMO...
Page 22: ...MEMO...
Page 27: ...1 5 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 42: ...1 20 MELSEC A 1 PRODUCT OUTLINE MEMO...
Page 52: ...2 10 MELSEC A 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MEMO...
Page 111: ...5 21 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 115: ...5 25 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 123: ...5 33 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 127: ...5 37 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 167: ...5 77 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 193: ...5 103 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 276: ...5 186 MELSEC A 5 DATA USED FOR POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 332: ...7 18 MELSEC A 7 MEMORY CONFIGURATION AND DATA PROCESS MEMO...
Page 334: ...MEMO...
Page 422: ...9 64 MELSEC A 9 MAIN POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 446: ...10 24 MELSEC A 10 ADVANCED POSITIONING CONTROL MEMO...
Page 472: ...11 26 MELSEC A 11 MANUAL CONTROL MEMO...
Page 576: ...12 104 MELSEC A 12 CONTROL AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS MEMO...
Page 745: ......