Chapter 12
•
•
•
•
Chapter 12
Adjust PID1 control
• When response is not stabilized in PID function
operation, adjust according to the following
procedure.
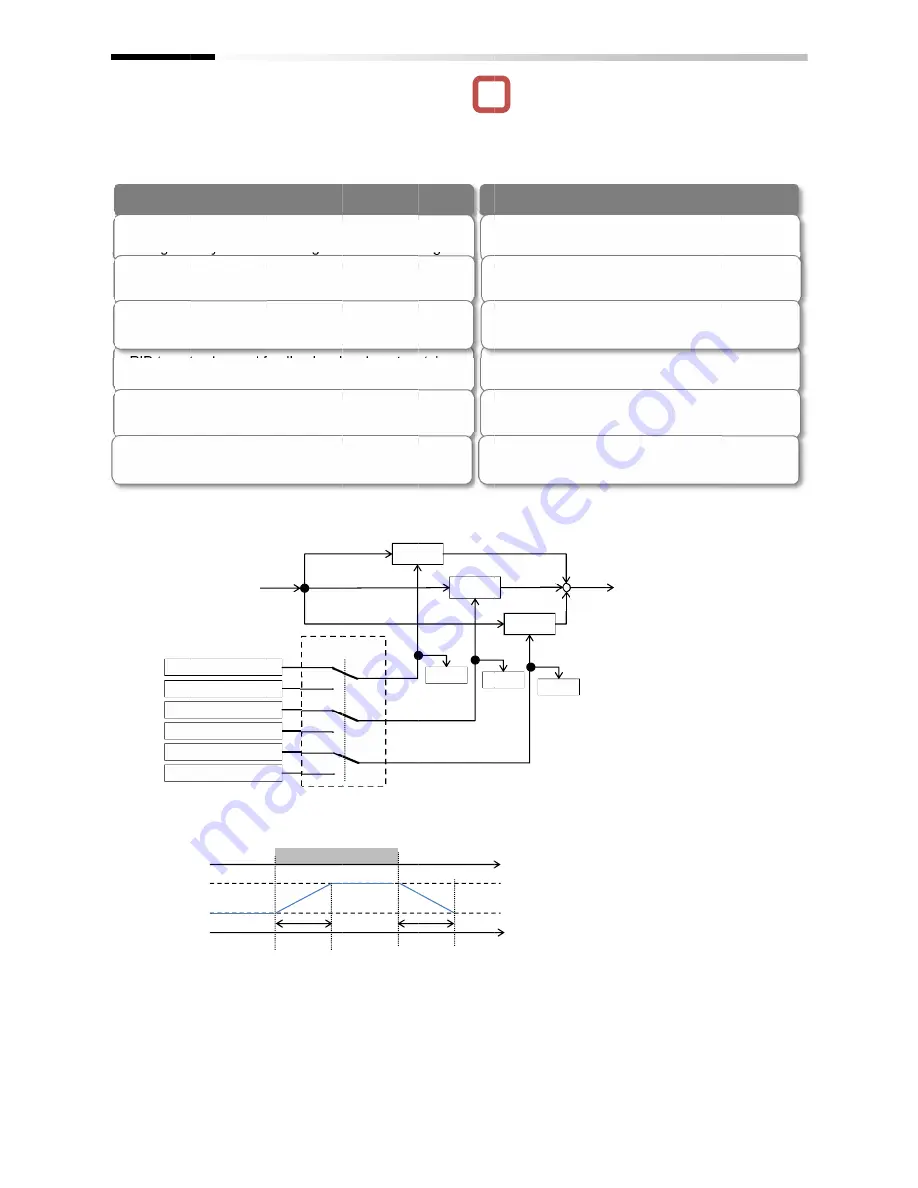
Control by switching PID1 gain
• PID gain 1 and 2 can be switched by switching the
input terminal function 055
• PID gain is time for PID1 gain to switch [AH
switches continuously.
• Output response is slow and feedback value does not
change swiftly
• Feedback value changes swiftly and is not stabilized.
• Overshooting or hunting occurs.
• PID target value and feedback value do not match
easily.
• Feedback
• t takes time for operation to be stabilized.
• Response is slow
• Small hunting occurs.
• Response due to disturbance is large and it takes time
until stabilization.
PID deviation
Proportional gain 1
Proportional gain 2
Integral
Integral
Differential
Differential
PRO
Gain 2
Gain 1
Chapter 12
Adjust PID1 control
When response is not stabilized in PID function
operation, adjust according to the following
procedure.
Control by switching PID1 gain
PID gain 1 and 2 can be switched by switching the
input terminal function 055
PID gain is time for PID1 gain to switch [AH
switches continuously.
Phenomenon
Output response is slow and feedback value does not
change swiftly even if PID target value was changed.
Feedback value changes swiftly and is not stabilized.
Overshooting or hunting occurs.
PID target value and feedback value do not match
Feedback value vibrates mildly.
t takes time for operation to be stabilized.
Response is slow even if proportional gain was increased.
Small hunting occurs.
Response due to disturbance is large and it takes time
until stabilization.
PID deviation
Proportional gain 1
[AH-61]
Proportional gain 2
[AH-64]
Integral gain 1 [AH-62]
Integral gain 2 [AH-65]
Differential gain 1
[AH-63]
Differential gain 2
[AH-66]
When response is not stabilized in PID function
operation, adjust according to the following
Control by switching PID1 gain
PID gain 1 and 2 can be switched by switching the
input terminal function 055 [PRO].
PID gain is time for PID1 gain to switch [AH
Phenomenon
►
Output response is slow and feedback value does not
even if PID target value was changed.
Feedback value changes swiftly and is not stabilized.
Overshooting or hunting occurs.
PID target value and feedback value do not match
value vibrates mildly.
t takes time for operation to be stabilized.
even if proportional gain was increased.
Response due to disturbance is large and it takes time
[PRO] terminal
Proportional gain 1
Proportional gain 2
62]
65]
gain 1
gain 2
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
[AH-67]
12
When response is not stabilized in PID function
operation, adjust according to the following
PID gain 1 and 2 can be switched by switching the
PID gain is time for PID1 gain to switch [AH-67] and
►
Output response is slow and feedback value does not
even if PID target value was changed.
Feedback value changes swiftly and is not stabilized.
PID target value and feedback value do not match
t takes time for operation to be stabilized.
even if proportional gain was increased.
Response due to disturbance is large and it takes time
[PRO] terminal
P control
ON
[AH
12-10-14
When response is not stabilized in PID function
PID gain 1 and 2 can be switched by switching the
67] and
• If acceleration/deceleration time is set too long,
following of output frequency will be
control may not be successful. In this case, set the
acceleration/deceleration time short.
• In the case of using the [PRO] terminal, set 01 to
PID1 gain switch method selection [AH
• Each gain selected
respective monitors [db
!
Output response is slow and feedback value does not
even if PID target value was changed.
•
Feedback value changes swiftly and is not stabilized.
•
PID target value and feedback value do not match
•
•
even if proportional gain was increased.
•
Response due to disturbance is large and it takes time
•
P control
I control
[db-61]
[db
[AH-67]
14
If acceleration/deceleration time is set too long,
following of output frequency will be
control may not be successful. In this case, set the
acceleration/deceleration time short.
In the case of using the [PRO] terminal, set 01 to
PID1 gain switch method selection [AH
Each gain selected
respective monitors [db
!
Examples of measures
Increase PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH
Increase PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH
Increase PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH
+
I control
D control
+
[db-62]
[db-63]
If acceleration/deceleration time is set too long,
following of output frequency will be
control may not be successful. In this case, set the
acceleration/deceleration time short.
In the case of using the [PRO] terminal, set 01 to
PID1 gain switch method selection [AH
Each gain selected for PIDs can be checked by
respective monitors [db-61] to [db
Examples of measures
Increase PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH
Increase PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH
Increase PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH
Result of PID
calculation
+
63]
Inverter Functions
If acceleration/deceleration time is set too long,
following of output frequency will be delayed and
control may not be successful. In this case, set the
acceleration/deceleration time short.
In the case of using the [PRO] terminal, set 01 to
PID1 gain switch method selection [AH
for PIDs can be checked by
61] to [db-63].
Examples of measures
Increase PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH
Increase PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH
Increase PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH
Decrease PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH
Result of PID
calculation
Inverter Functions
If acceleration/deceleration time is set too long,
delayed and
control may not be successful. In this case, set the
In the case of using the [PRO] terminal, set 01 to
PID1 gain switch method selection [AH-60].
for PIDs can be checked by
63].
Increase PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH-61].
Decrease PID1 proportional (P) gain 1 [AH-61].
Decrease PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH-62].
Increase PID1 integral (I) gain 1 [AH-62].
Increase PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH-63].
Decrease PID1 differential (D) gain 1 [AH-63].
Inverter Functions
control may not be successful. In this case, set the
Summary of Contents for SJ Series
Page 39: ...5 4 Chapter 5 Included Items Memo ...
Page 55: ...6 16 Chapter 6 Installation Memo ...
Page 91: ...7 36 Chapter 7 Wire Connection and Optional Devices Memo ...
Page 135: ...9 40 Chapter 9 Operating Instructions Memo ...
Page 145: ...10 10 Chapter 10 Test Run Memo ...
Page 159: ...12 2 6 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 169: ...12 3 10 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 195: ...12 5 8 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 217: ...12 8 12 Chapter 12 Inverter Function Memo ...
Page 287: ...12 10 32 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 303: ...12 11 16 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 349: ...12 15 8 Chapter 12 Inverter Function Memo ...
Page 395: ...12 17 34 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 397: ...12 18 2 Chapter 12 Inverter Functions Memo ...
Page 415: ...12 19 18 Chapter 12 Inverter Function Memo ...
Page 581: ...15 10 Chapter 15 Optional Cassettes Memo ...
Page 591: ...16 10 Chapter 16 ProDriveNext EzSQ Memo ...
Page 642: ...18 49 Chapter 18 Tips FAQ Troubleshooting Memo ...
Page 650: ...19 8 Chapter 19 Maintenance and Inspection Memo ...
Page 781: ...Appendix 1 70 Appendix 1 List of Parameters Memo ...
















































