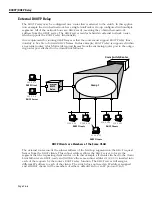
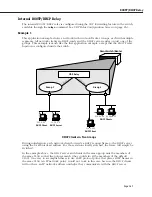
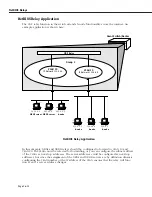
Path MTU Discovery
Page 25-42
Path MTU Discovery
All Gigabit Ethernet modules and all Mammoth-based Ethernet modules on the Omni
Switch/Router in Release 4.0 and later support path Maximum Transmission Unit (
MTU
)
discovery. In path
MTU
discovery, the Ethernet frame (datagram) size is set to the largest size
that does not require fragmentation anywhere along the path from a source host to its desti-
nation. This frame size, known as a Path
MTU
(
PMTU
), is thus equal to the minimum of the
MTUs
of each hop in the path.
♦
Note
♦
MTU
discovery is
not
supported on token ring,
FDDI
,
WAN
, or non-Mammoth Ethernet modules. However,
token ring and
FDDI
can be used as intermediate links
(e.g., trunking or bridging) between remote switches.
Path
MTU
discovery is active all of the time and is part of the switch’s operating system; you
do not need configure it.
The source host initially assumes that the
PMTU
of a path is the
MTU
of the first hop. It sends
all datagrams with the “Don’t Fragment” (
DF
) bit set. If a switch/router along the path receives
a datagram that is too large to forward without fragmentation, the following steps will be
executed:
1.
The switch/router that cannot forward these datagrams (i.e., the constricting hop) will
discard them.
2.
The constricting hop will send
ICMP
destination unreachable messages to the source host
with a code that indicates fragmentation is needed and the “Don’t Fragment” (
DF
) bit in
the Internet Protocol (
IP
) header has been set. This message (known as a “Datagram Too
Big” message) contains the
PMTU
of the constricting hop.
3.
After receiving a “Datagram Too Big” message, the source host reduces the size of the
MTU
so it matches the
PMTU
of the constricting hop.
4.
The
MTU
discovery process ends when datagrams can be sent without fragmentation.
However, the source host will
not
reduce the size of a datagram below 68 octets.
Summary of Contents for Omni Switch/Router
Page 1: ...Part No 060166 10 Rev C March 2005 Omni Switch Router User Manual Release 4 5 www alcatel com ...
Page 4: ...page iv ...
Page 110: ...WAN Modules Page 3 40 ...
Page 156: ...UI Table Filtering Using Search and Filter Commands Page 4 46 ...
Page 164: ...Using ZMODEM Page 5 8 ...
Page 186: ...Displaying and Setting the Swap State Page 6 22 ...
Page 202: ...Creating a New File System Page 7 16 ...
Page 270: ...Displaying Secure Access Entries in the MPM Log Page 10 14 ...
Page 430: ...OmniChannel Page 15 16 ...
Page 496: ...Configuring Source Route to Transparent Bridging Page 17 48 ...
Page 542: ...Dissimilar LAN Switching Capabilities Page 18 46 ...
Page 646: ...Application Example DHCP Policies Page 20 30 ...
Page 660: ...GMAP Page 21 14 ...
Page 710: ...Viewing the Virtual Interface of Multicast VLANs Page 23 16 ...
Page 722: ...Application Example 5 Page 24 12 ...
Page 788: ...Viewing UDP Relay Statistics Page 26 24 ...
Page 872: ...The WAN Port Software Menu Page 28 46 ...
Page 960: ...Deleting a PPP Entity Page 30 22 ...
Page 978: ...Displaying Link Status Page 31 18 ...
Page 988: ...Displaying ISDN Configuration Entry Status Page 32 10 ...
Page 1024: ...Backup Services Commands Page 34 14 ...
Page 1062: ...Diagnostic Test Cable Schematics Page 36 24 ...
Page 1072: ...Configuring a Switch with an MPX Page A 10 ...
Page 1086: ...Page B 14 ...
Page 1100: ...Page I 14 Index ...