AutoTracker VLANs
Page 22-12
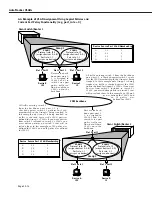
The Usefulness of Port Policies
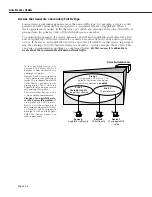
As has been explained – and as illustrated on page 22-10 – original port policy functionality is
not well-suited to the creation of consistent
VLAN
membership
in a multi-switch environment.
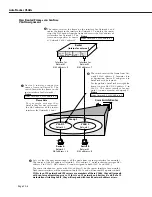
Current port policy functionality – as illustrated on page 22-11 – neither contributes to nor
participates in
VLAN
assignments. Port policies, either original or current, are in fact not useful
in the creation of consistent
VLAN
membership
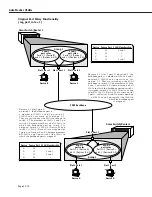
across multiple switches. Logical policies are
of far greater use, as illustrated on page 22-13. So, why use port policies at all?
Port Policies are Useful in these Situations:
•
Silent stations
. If a device does not transmit traffic (such as a printer), the port to which the
device is connected never gets assigned to
VLAN
s. It is then impossible for other stations to
communicate with that device. Creating a port policy that assigns the silent device’s port to
one or more
VLAN
s will enable traffic to flow out that port to the silent device.
•
Inactive
VLAN
s
. AutoTracker does not activate a
VLAN
– or its internal router – until a port is
assigned to that
VLAN
. AutoTracker assigns ports to
VLAN
s with port policies immediately.
However, AutoTracker only assigns ports to
VLAN
s with logical policies when a frame is
received from a source device that matches the
VLAN
’s policies. This means that, in some
network situations, you may need to assign a port policy to a
VLAN
to force it active.
Appli-
cation Example 5
in Chapter 24 provides an example of this.
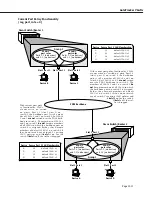
•
Backbone connections
. A port policy that assigns the backbone port to a
VLAN
will enable
traffic from that
VLAN
to flow out onto the backbone.
♦
Important Note
♦
If you are using port policies to extend
VLAN
s across a backbone, you
are strongly advised to use current (default) port policy functionality. If
you use original port policy functionality, you are, in effect, placing all
devices learned from the backbone port into the same
VLAN
. If the port
policy is configured for all
VLAN
s (so that all
VLAN
s can communicate
over the backbone), all devices learned from the backbone port are
assigned to all
VLAN
s. This is not desirable – it would subject locally-
connected devices to all the backbone traffic.
Summary of Contents for Omni Switch/Router
Page 1: ...Part No 060166 10 Rev C March 2005 Omni Switch Router User Manual Release 4 5 www alcatel com ...
Page 4: ...page iv ...
Page 110: ...WAN Modules Page 3 40 ...
Page 156: ...UI Table Filtering Using Search and Filter Commands Page 4 46 ...
Page 164: ...Using ZMODEM Page 5 8 ...
Page 186: ...Displaying and Setting the Swap State Page 6 22 ...
Page 202: ...Creating a New File System Page 7 16 ...
Page 270: ...Displaying Secure Access Entries in the MPM Log Page 10 14 ...
Page 430: ...OmniChannel Page 15 16 ...
Page 496: ...Configuring Source Route to Transparent Bridging Page 17 48 ...
Page 542: ...Dissimilar LAN Switching Capabilities Page 18 46 ...
Page 646: ...Application Example DHCP Policies Page 20 30 ...
Page 660: ...GMAP Page 21 14 ...
Page 710: ...Viewing the Virtual Interface of Multicast VLANs Page 23 16 ...
Page 722: ...Application Example 5 Page 24 12 ...
Page 788: ...Viewing UDP Relay Statistics Page 26 24 ...
Page 872: ...The WAN Port Software Menu Page 28 46 ...
Page 960: ...Deleting a PPP Entity Page 30 22 ...
Page 978: ...Displaying Link Status Page 31 18 ...
Page 988: ...Displaying ISDN Configuration Entry Status Page 32 10 ...
Page 1024: ...Backup Services Commands Page 34 14 ...
Page 1062: ...Diagnostic Test Cable Schematics Page 36 24 ...
Page 1072: ...Configuring a Switch with an MPX Page A 10 ...
Page 1086: ...Page B 14 ...
Page 1100: ...Page I 14 Index ...