How Ports Are Assigned to Groups
Page 19-2
How Ports Are Assigned to Groups
There are two methods for assigning physical OmniS/R ports to a Group. One method is
static and requires manual configuration by the network administrator; the other method is
dynamic and requires only the configuration of AutoTracker rules for port assignment to
occur. The two methods are described in this section.
Static Port Assignment
In the static method, the network administrator manually assigns a port to a Group through
the
crgp
and
addvp
commands. The static method can be restrictive because it limits the
mobility of users in a multi-Group network. Users can only move within their assigned
Group. In addition, customized access for individual users is limited by this method. You can
use the static method of port assignment with mobile and non-mobile groups. Static port
assignment can be combined with dynamic port assignment for mobile groups, while static
port assignment is the only method for assigning ports to non-mobile groups.
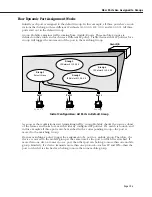
Dynamic Port Assignment (Group Mobility)
The dynamic method is available with the Group Mobility feature. Initially each port is part of
the default Group #1 (only ports in the default Group and ports in mobile Groups are candi-
dates for dynamic port assignment). Based on the nature of traffic and configured
AutoTracker policies, ports are dynamically assigned to the appropriate Group.
For example, if a device attached to a port transmits traffic from the 140.0.0.0 subnet,
AutoTracker will check to see if a policy exists for this IP address. If it does, then it will move
the port from the default Group to the first Group using this policy. If this device detaches
from the network the port will be re-assigned to a Group without intervention by the network
administrator.
A port can belong to multiple mobile groups (up to 16) as long as devices attached to that
port match policies of these mobile groups. However, an individual device, or MAC address,
can only belong to one mobile group per protocol.
The dynamic method of port-to-Group assignment still requires the creation of Groups
through the
crgp
command. The criteria for the dynamic assignment of ports to a Group are
determined by AutoTracker policies that you can configure during the
crgp
procedure.
Only Ethernet ports can be dynamically assigned to Groups.
If more than one Group has the same type of rule, then ports matching that policy will be
assigned to the first Group matching the policy. For example, if a device matched policies in
both Groups 2 and 5, the port would be assigned to Group 2. To make the most out of
Group Mobility it is best not to duplicate policies among Groups.
Configuring Dynamic Port Assignment
You can enable dynamic port assignment while creating a group through the
crgp
command.
During the
crgp
procedure, you will be prompted
Enable Group Mobility on the Group ? [y/n] (n):
Answer
Yes
to this question to give this Group the capability of having ports and devices
dynamically added to the Group. Port and devices will be dynamically assigned based on
AutoTracker rules you define.
Service Ports and Group Mobility
These ports may be automatically added to the mobile group during the
crgp
procedure or
through the
cats
command.
Summary of Contents for Omni Switch/Router
Page 1: ...Part No 060166 10 Rev C March 2005 Omni Switch Router User Manual Release 4 5 www alcatel com ...
Page 4: ...page iv ...
Page 110: ...WAN Modules Page 3 40 ...
Page 156: ...UI Table Filtering Using Search and Filter Commands Page 4 46 ...
Page 164: ...Using ZMODEM Page 5 8 ...
Page 186: ...Displaying and Setting the Swap State Page 6 22 ...
Page 202: ...Creating a New File System Page 7 16 ...
Page 270: ...Displaying Secure Access Entries in the MPM Log Page 10 14 ...
Page 430: ...OmniChannel Page 15 16 ...
Page 496: ...Configuring Source Route to Transparent Bridging Page 17 48 ...
Page 542: ...Dissimilar LAN Switching Capabilities Page 18 46 ...
Page 646: ...Application Example DHCP Policies Page 20 30 ...
Page 660: ...GMAP Page 21 14 ...
Page 710: ...Viewing the Virtual Interface of Multicast VLANs Page 23 16 ...
Page 722: ...Application Example 5 Page 24 12 ...
Page 788: ...Viewing UDP Relay Statistics Page 26 24 ...
Page 872: ...The WAN Port Software Menu Page 28 46 ...
Page 960: ...Deleting a PPP Entity Page 30 22 ...
Page 978: ...Displaying Link Status Page 31 18 ...
Page 988: ...Displaying ISDN Configuration Entry Status Page 32 10 ...
Page 1024: ...Backup Services Commands Page 34 14 ...
Page 1062: ...Diagnostic Test Cable Schematics Page 36 24 ...
Page 1072: ...Configuring a Switch with an MPX Page A 10 ...
Page 1086: ...Page B 14 ...
Page 1100: ...Page I 14 Index ...