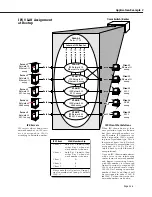
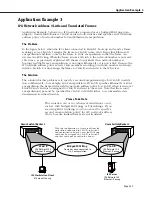
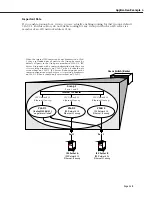
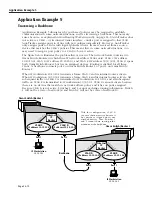
Setting Up IP Routing on the Switch
Page 25-4
Setting Up IP Routing on the Switch
IP routing is enabled on a per-port basis by creating a virtual IP router port for a group/
VLAN
.
The switch does not do any routing unless the virtual router port has IP routing enabled
(routing is enabled by default). The steps for setting up IP routing on the switch are given
here:
Step 1. Configuring a Virtual Router Port
A virtual router port may be created when you set up or modify a group/
VLAN
through the
crgp
command or
modvl
command described in Chapter 19, “Managing Groups and Virtual
Ports.” To create a virtual router port, enable IP routing and specify an IP address for the
router port.
When routing is enabled on the port, the switch creates routing tables and address transla-
tion tables so it knows how to forward traffic. The switch keeps track of router ports and any
other routers in the network. The switch uses the Address Resolution Protocol (
ARP
) to match
IP addresses with
MAC
addresses. It uses routing protocols, such as the Routing Information
Protocol (
RIP
), to determine the best path for forwarding traffic. (Other routing protocols are
available in the Advanced Routing software package.) It also periodically sends/receives rout-
ing messages to/from other routers to keep its routing tables updated.
♦
Important Note
♦
When Spanning Tree and IP routing are both enabled,
packets are not forwarded unless the Spanning Tree
Status for the port to which packets are to be
forwarded has progressed from Listening to Learning to
Forwarding. For example, if IP is enabled on
VLAN
42
that has ports 1/1-3 attached to it and you want to
forward to a host from port 1/2. Use the
vi 1/2
command to determine if the Spanning Tree Protocol
has entered the Forwarding state for that port.
Step 2. Configuring Optional IP Routing Parameters
Optional configuration for IP routing includes the following:
• Static routes. These are routes that are manually added to the routing table and may be
used rather than dynamic routes (which are learned through routing protocols like
RIP
).
•
RIP
filters. Controls the operation of
RIP
by minimizing the number of entries that will be
added to the routing table.
Static routes and
RIP
filters are described in this chapter. This chapter also describes how to
view various IP statistics as well as the routing table. It includes information about how to
ping another IP host in the network, how to telnet to a remote system, and how to trace an IP
route.
Summary of Contents for Omni Switch/Router
Page 1: ...Part No 060166 10 Rev C March 2005 Omni Switch Router User Manual Release 4 5 www alcatel com ...
Page 4: ...page iv ...
Page 110: ...WAN Modules Page 3 40 ...
Page 156: ...UI Table Filtering Using Search and Filter Commands Page 4 46 ...
Page 164: ...Using ZMODEM Page 5 8 ...
Page 186: ...Displaying and Setting the Swap State Page 6 22 ...
Page 202: ...Creating a New File System Page 7 16 ...
Page 270: ...Displaying Secure Access Entries in the MPM Log Page 10 14 ...
Page 430: ...OmniChannel Page 15 16 ...
Page 496: ...Configuring Source Route to Transparent Bridging Page 17 48 ...
Page 542: ...Dissimilar LAN Switching Capabilities Page 18 46 ...
Page 646: ...Application Example DHCP Policies Page 20 30 ...
Page 660: ...GMAP Page 21 14 ...
Page 710: ...Viewing the Virtual Interface of Multicast VLANs Page 23 16 ...
Page 722: ...Application Example 5 Page 24 12 ...
Page 788: ...Viewing UDP Relay Statistics Page 26 24 ...
Page 872: ...The WAN Port Software Menu Page 28 46 ...
Page 960: ...Deleting a PPP Entity Page 30 22 ...
Page 978: ...Displaying Link Status Page 31 18 ...
Page 988: ...Displaying ISDN Configuration Entry Status Page 32 10 ...
Page 1024: ...Backup Services Commands Page 34 14 ...
Page 1062: ...Diagnostic Test Cable Schematics Page 36 24 ...
Page 1072: ...Configuring a Switch with an MPX Page A 10 ...
Page 1086: ...Page B 14 ...
Page 1100: ...Page I 14 Index ...