AutoTracker VLANs
Page 22-6
Devices that Generate a Secondary Traffic Type
Source devices sometimes generate more than one traffic type; for example, a device could
generate
IP
traffic primarily but also generate a secondary stream of AppleTalk. When a
device generates secondary traffic that does not match any existing
VLAN
policy, that traffic is
grouped into the primary
VLAN
of which the device is a member.
To continue the example, if a device generates both
IP
and AppleTalk, and both an
IP
VLAN
and an AppleTalk
VLAN
exist, that device is made a member of both
VLAN
s and no problem
occurs. If, however, an AppleTalk
VLAN
does not exist, all traffic from that device is grouped
into the existing
VLAN
of which the device is a member – in this example, the
IP
VLAN
. This
can cause communication problems, as explained below.
For this reason, it is advisable to
create
VLAN
s that accommodate all known network traffic.
Omni Switch/Router
12345678
123456
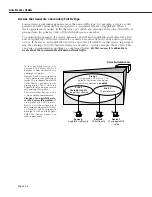
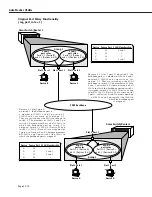
In this example Device A is
assigned to default
VLAN
#1
because it does not match any
existing
VLAN
policy.
Devices B and C are assigned to
VLAN
2 because they generate
IP
traffic. The secondary AppleTalk
traffic Device C generates is also
grouped into
VLAN
2, since the
AppleTalk traffic does not match
any existing
VLAN
policy.
The result is that Devices A and
C are unable to communicate.
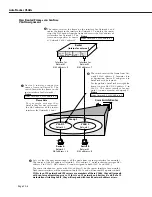
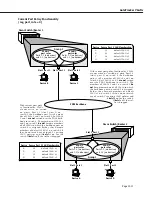
Creation of an AppleTalk proto-
col
VLAN
solves this problem.
If
a n A p p l e T a l k
V L A N
e x i s t s ,
Device A will be assigned to it
and removed from Default
VLAN
#1. Device C will be assigned to
both the
IP
VLAN
and the Apple-
Talk
VLAN
. Devices A and C can
then communicate.
VLAN
1
(default
VLAN
#1)
no policies allowed
VLAN
2
IP
protocol
VLAN
Group 2
A s s i g n m e n t o f d e v i c e s t o
default
VLAN
when they do not
match any policies is
enabled
.
Device B
IP
traffic only
Device A
AppleTalk traffic only
Device C
IP
and AppleTalk
traffic
Summary of Contents for Omni Switch/Router
Page 1: ...Part No 060166 10 Rev C March 2005 Omni Switch Router User Manual Release 4 5 www alcatel com ...
Page 4: ...page iv ...
Page 110: ...WAN Modules Page 3 40 ...
Page 156: ...UI Table Filtering Using Search and Filter Commands Page 4 46 ...
Page 164: ...Using ZMODEM Page 5 8 ...
Page 186: ...Displaying and Setting the Swap State Page 6 22 ...
Page 202: ...Creating a New File System Page 7 16 ...
Page 270: ...Displaying Secure Access Entries in the MPM Log Page 10 14 ...
Page 430: ...OmniChannel Page 15 16 ...
Page 496: ...Configuring Source Route to Transparent Bridging Page 17 48 ...
Page 542: ...Dissimilar LAN Switching Capabilities Page 18 46 ...
Page 646: ...Application Example DHCP Policies Page 20 30 ...
Page 660: ...GMAP Page 21 14 ...
Page 710: ...Viewing the Virtual Interface of Multicast VLANs Page 23 16 ...
Page 722: ...Application Example 5 Page 24 12 ...
Page 788: ...Viewing UDP Relay Statistics Page 26 24 ...
Page 872: ...The WAN Port Software Menu Page 28 46 ...
Page 960: ...Deleting a PPP Entity Page 30 22 ...
Page 978: ...Displaying Link Status Page 31 18 ...
Page 988: ...Displaying ISDN Configuration Entry Status Page 32 10 ...
Page 1024: ...Backup Services Commands Page 34 14 ...
Page 1062: ...Diagnostic Test Cable Schematics Page 36 24 ...
Page 1072: ...Configuring a Switch with an MPX Page A 10 ...
Page 1086: ...Page B 14 ...
Page 1100: ...Page I 14 Index ...